
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school

-
 Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
-
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle

-
 Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
-
Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote

-
 Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
-
UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall

-
 Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
-
New Zealand deputy PM defends claims colonisation good for Maori

-
 Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
-
Deadly storm sparks floods in Spain, raises calls to postpone Portugal vote

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
-
Lower pollution during Covid boosted methane: study

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
-
Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending

-
 Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
-
Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links

-
 ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
-
Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal

-
 ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
-
What does Iran want from talks with the US?

-
 Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
-
Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election

-
 Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
-
Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls

-
 Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
-
BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover

-
 UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
-
Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics

-
 Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
-
Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast

-
 Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
-
German factory orders rise at fastest rate in 2 years in December

-
 Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
-
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation

-
 Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment
-
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club

-
 Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
Barry Manilow cancels Las Vegas shows but 'doing great' post-surgery
-
Rising euro, falling inflation in focus at ECB meeting


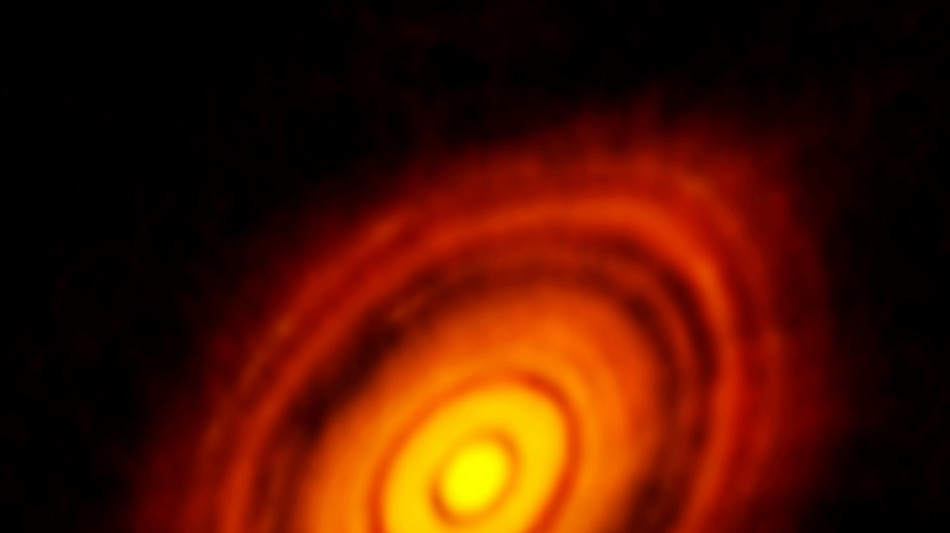
James Webb telescope discovers its first exoplanet
The James Webb Space Telescope has discovered its first exoplanet, astronomers said Wednesday, capturing rare direct images of the relatively small world in the Earth's galactic backyard.
The telescope, which can see farther into the universe than anything before it, has turbocharged the search for planets beyond the Solar System since coming online in 2022.
Until now, however, its deep gaze has mostly been used to probe already known exoplanets -- to find out key information such as the atmospheric composition -- rather than tracking down new worlds.
The discovery of exoplanet TWA 7b, revealed in a study in the journal Nature, "represents a first for the telescope", France's CNRS research centre said in a statement.
The large majority of the nearly 6,000 exoplanets found so far have been identified from the light they blot out when they pass in front of their star, rather than from direct images of the planet.
Webb "has spent an enormous amount of time observing planets that have never been directly imaged," lead study author Anne-Marie Lagrange of the Paris Observatory told AFP.
- 'Blinded by the light' -
Capturing direct images of faraway planets is difficult because they are "very faint" due to a lack of heat, Lagrange said. Even worse, she added, "we're blinded by the light of the star they orbit."
But Webb has a way to get around the problem.
An attachment to Webb's MIRI instrument called a coronagraph masks the star, creating an effect similar to a solar eclipse. The telescope's infrared vision can then peer through and spot the planet.
Astronomers pointed Webb at the star TWA 7, which is around a hundred light years from Earth -- relatively nearby in the universe.
The star, which was first spotted by the Hubble space telescope in 1999, was thought to be a promising target for two reasons.
It is just 6.4 million years old -- a baby compared to the Sun's 4.5 billion years -- and still surrounded by a massive disc of gas and dust where planets are thought to form.
And from the direction of Earth, the disc is seen from above, giving a good view of its rings.
The three rings around the star, which stretch more than 100 times the distance separating the Sun and Earth, had previously been spotted by the Very Large Telescope in Chile.
But inside an otherwise empty section of the second ring, the Webb telescope detected something particularly bright.
Astronomers ruled out that the light was coming from an object at the edge of the Solar System, or from a distant galaxy behind the star.
That could mean only that the light source was a relatively small and cold planet, with a mass at least 10 times lighter than any other exoplanet directly imaged so far, according to the study.
- The hunt for smaller worlds -
The researchers estimated that the planet's mass was similar to that of Saturn, a gas giant that weighs only a third of Jupiter, the biggest planet in the Solar System.
Webb has increased the ability to detect exoplanets via direct images by a factor of 10, Lagrange said.
That is important because smaller, rocky planets similar to Earth or Mars are the ultimate target in the search for habitable worlds outside of the Solar System.
Lagrange said she would be delighted to discover "Earth-like planets" one day.
But she said astronomers needed to study all kinds of planets -- and to understand how planetary systems form -- to know whether the life-hosting Solar System is unique.
In the future, astronomers expect the Webb telescope will be able to spot planets even smaller than TWA 7b.
But directly capturing images of faraway worlds similar to Earth will require even more telescopic power, such as from he Extremely Large Telescope that is scheduled to come online in Chile in 2028.
P.Kolisnyk--CPN


