
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents

-
 Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
-
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks

-
 Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
-
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection

-
 Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users
-
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo

-
 Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
-
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles

-
 Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer

-
 Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns
-
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost

-
 Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift
-
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe

-
 In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school
-
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters

-
 As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle
-
Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts

-
 Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote
Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote
-
Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant

-
 UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall
UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall
-
Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer

-
 New Zealand deputy PM defends claims colonisation good for Maori
New Zealand deputy PM defends claims colonisation good for Maori
-
Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb

-
 Deadly storm sparks floods in Spain, raises calls to postpone Portugal vote
Deadly storm sparks floods in Spain, raises calls to postpone Portugal vote
-
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric

-
 Lower pollution during Covid boosted methane: study
Lower pollution during Covid boosted methane: study
-
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate

-
 Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending
Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending
-
Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid

-
 Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links
Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links
-
ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates

-
 Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal
Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal
-
ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters

-
 What does Iran want from talks with the US?
What does Iran want from talks with the US?
-
Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025

-
 Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election
Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election
-
Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls

-
 Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
-
Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls

-
 BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover
BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover
-
UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief

-
 Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics
Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics
-
Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK

-
 Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast
Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast
-
Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices

-
 German factory orders rise at fastest rate in 2 years in December
German factory orders rise at fastest rate in 2 years in December
-
Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech


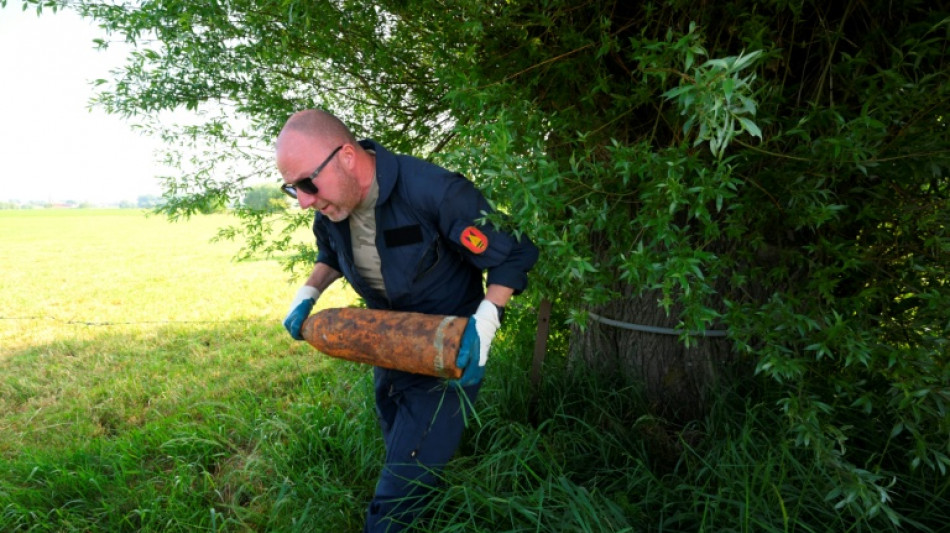
Deminers comb Belgian countryside for remnants of Great War
Working with the utmost care, a Belgian deminer wiggled a century-old artillery shell from the soil and deposited it safely in a sandbox in the back of his truck.
"This one's an 18-pounder -- there might be a bit of explosive left inside," said Franjo, one of a team of army specialists whose job is to comb the countryside for remnants of the Great War.
In the flat fields of northwestern Belgium, where hundreds of thousands of soldiers fell between 1914 and 1918, traces of the conflict are everywhere.
Beyond the military cemeteries -- their neat rows of tombstones stretching sometimes beyond the line of sight -- British, German and French shells and munitions are constantly turning up at the surface.
The task of tracking and removing them keeps the demining service of the Belgian army -- known as SEDEE in French, DOVO in Flemish -- busy on a daily basis.
Founded in the wake of World War I, the service concentrates its activities around the town of Langemark-Poelkapelle, north of Ypres, where it has set up base.
Each year its teams respond to more than 2,000 requests from farmers or construction crews to remove munitions -- some spent, but others still live -- after turning the soil to sow crops or lay foundations for a new home.
Once removed, the team determines how dangerous the munitions are -- and based on that how to dispose of them, either detonating them outside, or burning them in an oven.
"We destroy 200 to 250 tonnes every year," Jacques Callebaut, head of public relations for the deminer service, told AFP.
On this morning near Ypres, it took the team under an hour to scoop up a dozen shells and grenades -- snaking along little country roads with their small truck.
Franjo -- who asked to be identified by first name only -- and his two teammates navigate with the help of a small pile of printed police emails, mapping all the spots where potential explosives have been flagged.
- 'An added danger' -
Sometimes landowners try to make their work easier by setting out the shells to be collected from the roadside.
The deminers themselves wear thick gloves to handle the rusted relics, which can potentially contain white phosphorus, arsenic or mustard gas -- a chemical weapon causing skin blistering also known as yperite because of its use near Ypres in World War I.
"Around 60 percent of the munitions we find contain an explosive load, and around 10 to 30 can also be toxic, which brings an added danger," Callebaut said.
When in doubt, they rely on technology -- peering inside the shell with X-rays to spot a smoke cartridge, or using a neuron spectrometer to analyse its various materials.
Belgium's deminers have built up a degree of expertise that other countries have come to rely on.
"We handle the toxic munitions found in The Netherlands, and a few weeks ago we were called to neutralise a bomb in Norway as they didn't have the equipment to do so," Callebaut said.
At the crossroads of the Germanic, French and British empires, Belgium has been a key battlefield since the European Middle Ages -- and famously saw Napoleon's French army defeated by the British at Waterloo, in 1815.
It was heavily hit by the two world wars of the 20th century -- but it was the first that left by far the most traces in the land.
"World War II shells only turn up from time in time, in cities that came under bombardment," said Corentin Rousman, a Belgian historian.
Near Ypres, by contrast, "there was a static front line for four years, with millions of shells on either side," he said.
O.Ignatyev--CPN


