
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease

-
 As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese
-
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
 Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut
-
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge

-
 Wheelchair user flies into space, a first
Wheelchair user flies into space, a first
-
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women

-
 US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack
-
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike

-
 US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide
-
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah

-
 Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain
-
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech

-
 Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant
-
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM

-
 Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters
-
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high

-
 Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims
-
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers

-
 Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears
-
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law

-
 EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force
-
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award

-
 Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care
-
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms

-
 Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels
-
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters

-
 US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners
-
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty

-
 Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company
-
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce

-
 Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit
-
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling

-
 ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future
-
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides

-
 Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?
-
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick

-
 EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
-
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026

-
 Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount
-
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win

-
 What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal
-
Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation

-
 ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future
ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future
-
EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom
Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom
-
Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race

-
 CNN's future unclear as Trump applies pressure
CNN's future unclear as Trump applies pressure
-
German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases


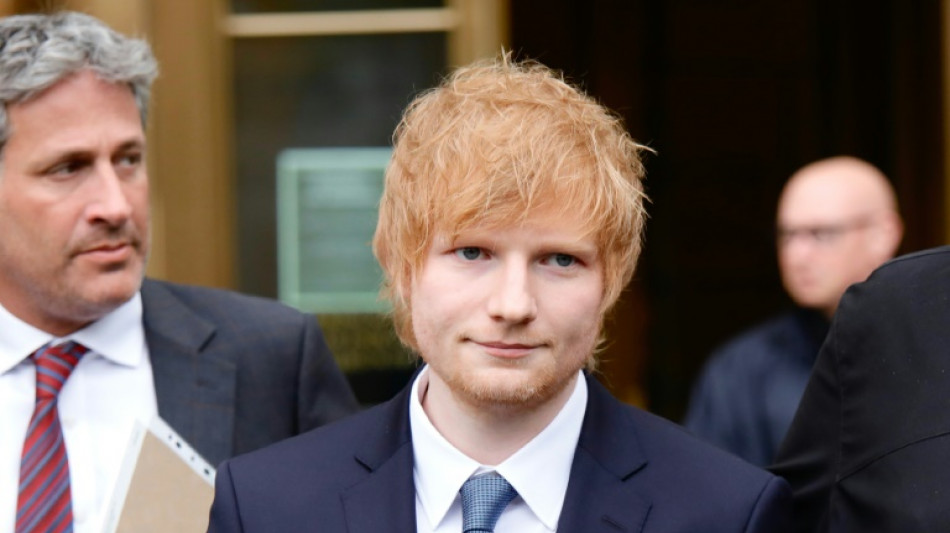
Sheeran copyright battle could stoke songwriting paranoia
Ed Sheeran is preparing for a blockbuster tour and album release amid regular trips to Manhattan's federal court, where he's defending his songwriting in a closely watched copyright case.
The trial centers on whether the British pop phenom plagiarized Marvin Gaye's 1973 soul classic "Let's Get It On" in his 2014 hit "Thinking Out Loud."
The heirs of Ed Townsend, who co-wrote Gaye's smash, are behind the civil suit, and allege "striking similarities and overt common elements" between the songs.
It's the latest in a series of high-profile music copyright cases that have the industry on edge, leaving some songwriters paranoid about their own creative processes and vulnerability to litigation.
Sheeran, 32, has spent days testifying with guitar in hand, playing demos for the court to prove the 1-3-4-5 chord progression that's primarily in question is a basic building block of pop music that can't be owned.
His legal team argues that Gaye and Townsend were far from the first to record it, citing, for example, a number of Van Morrison songs that use the sequence and that were released prior to "Let's Get It On."
It's a notion echoed by forensic musicologist Joe Bennett.
"The world I want to live in is one where nobody sues anyone for a one- or two-bar melodic or harmonic similarity, because those similarities can so easily occur through coincidence," the professor at Massachusetts' Berklee College of Music told AFP.
"They shouldn't be protectable by copyright."
The case hinges on the actual composition of the songs rather than the recorded versions -- think sheet music, not vibes.
In theory that's a specificity that could help Sheeran's case, but once a music copyright suit reaches the point of jury trial, anything can happen.
Winning demands significant funding and resources, and defendants are beholden to the volatility of opinions from jury members who almost certainly don't have a background in musicology.
Both sides have hired expert witnesses to explain the technical details to jurors, but, of course, their conclusions differ significantly.
"If you play music to a jury, it could go either way," Bennett said.
- 'Chilling effect' -
There have been a handful of landmark music copyright cases in recent years, notably in 2016 when Gaye's family -- who is not part of the New York lawsuit against Sheeran -- successfully sued the artists Robin Thicke and Pharrell Williams over similarities between the song "Blurred Lines" and Gaye's "Got to Give it Up."
The result surprised many in the industry, including legal experts, who considered many of the musical components cited as foundational, and existing largely in the public domain.
Shortly thereafter an appeals court decision confirmed Led Zeppelin's victory over a similar case centered on the classic "Stairway to Heaven" -- a boon for songwriters.
"One reason that this Ed Sheeran case may be really important to the industry is that it's a data point that would show well is the pendulum actually back on the other side, or are we just going back and forth?" said Joseph Fishman, a law professor specialized in intellectual property at Vanderbilt University.
"If it's going back and forth, that could still have a chilling effect on how songwriters write, because you never know -- is my case going to be the one?"
And unintended infringement is a weak defense: in 1976, George Harrison was found liable for "subconsciously" plagiarizing "He's So Fine" by the Chiffons for his first solo hit "My Sweet Lord."
In his memoir Harrison later wrote that he suffered a "paranoia about songwriting that had started to build up in me."
This week Sheeran told the court that fellow songwriters have told him "you have to win this for us" adding with a tone of exasperation that if the Townsend estate prevails, "I'm done."
"I find it really insulting to work my whole life... and have someone diminish it by saying that I stole it," Sheeran said on the stand Monday.
Bennett said many of his students at Berklee -- a prestigious conservatory of contemporary music -- have voiced concern over the Sheeran case, speaking as the next generation of songwriters.
One of them, 21-year-old Mary Jo Swank, told AFP that "I've definitely grown a fear that the idea of being completely original and unique is going to put the emotional and creative process of a songwriter in jeopardy."
"It'd be nice if I'd be allowed to write my take on a 1-3-4-5 progression without having to worry that it's not unique enough."
M.García--CPN


