-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount

-
 Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
-
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal

-
 Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
-
ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future

-
 EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
-
Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom

-
 Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
-
CNN's future unclear as Trump applies pressure

-
 German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases
German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases
-
EU's Mercosur trade deal hits French, Italian roadblock

-
 Warner Bros rejects Paramount bid, sticks with Netflix
Warner Bros rejects Paramount bid, sticks with Netflix
-
Crude prices surge after Trump orders Venezuela oil blockade

-
 Warner Bros. Discovery rejects Paramount bid
Warner Bros. Discovery rejects Paramount bid
-
Doctors in England go on strike for 14th time

-
 Ghana's Highlife finds its rhythm on UNESCO world stage
Ghana's Highlife finds its rhythm on UNESCO world stage
-
Stocks gain as traders bet on interest rate moves

-
 France probes 'foreign interference' after malware found on ferry
France probes 'foreign interference' after malware found on ferry
-
Europe's Ariane 6 rocket puts EU navigation satellites in orbit

-
 Bleak end to the year as German business morale drops
Bleak end to the year as German business morale drops
-
Hundreds queue at Louvre museum as strike vote delays opening

-
 Markets rise even as US jobs data fail to boost rate cut bets
Markets rise even as US jobs data fail to boost rate cut bets
-
Asian markets mixed as US jobs data fails to boost rate cut hopes

-
 Bondi shooting shocks, angers Australia Jewish community
Bondi shooting shocks, angers Australia Jewish community
-
UK experiences sunniest year on record


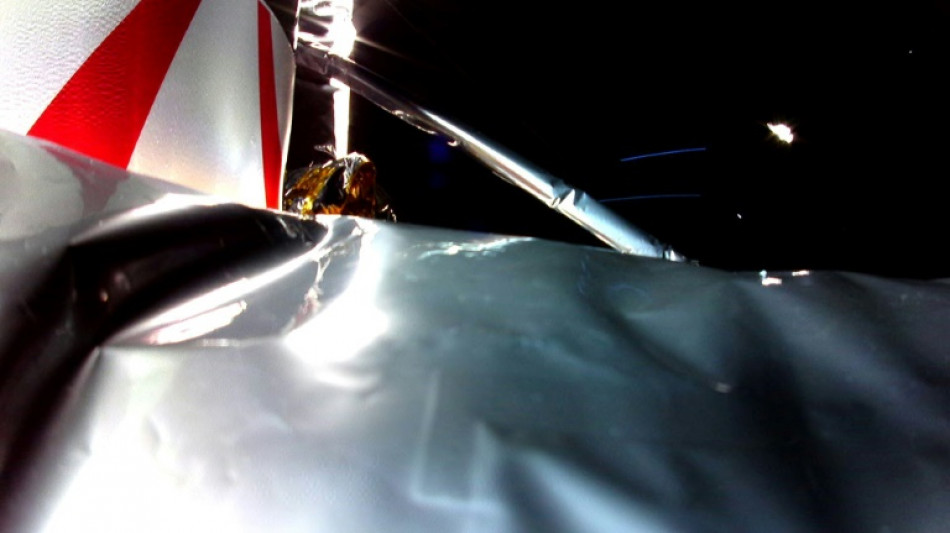
Doomed US lunar lander's space odyssey continues...for now
Is it the little spaceship that could?
A private US lunar lander that's been hemorrhaging fuel since an onboard explosion at the start of its journey is somehow still chugging along, snapping selfies and running science instruments as it continues its journey through space.
Though Astrobotic, the company that built the Peregrine robot, has said a controlled touchdown on the Moon is no longer possible, it hasn't ruled out a so-called "hard landing" or crash -- a prospect that has space watchers gripped.
"Peregrine has now been operating in space for more than 4 days," Astrobotic said in its latest update posted on X on Friday, adding it remained "stable and operational."
The rate of fuel loss has steadily diminished as the pressure inside its tank drops, meaning the company has been able to extend the spacecraft's life far longer than it initially thought possible.
Meanwhile, the US, German and Mexican space agencies have been able to power on the scientific instruments they wanted to run on the Moon.
"Measurements and operations of the NASA-provided science instruments on board will provide valuable experience, technical knowledge, and scientific data to future CLPS lunar deliveries," said Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for exploration for NASA.
Commercial Lunar Payload Services is the experimental NASA program under which the space agency paid Astrobotic more than $100 million to ship its hardware of Peregrine, as part of a strategy to seed a commercial lunar economy and reduce its own overheads.
Astrobotic is the third private entity to have failed in a soft landing, following an Israeli nonprofit and a Japanese company.
- 'Shots on goal' -
Though it hasn't worked out this time, NASA officials have made clear their strategy of "more shots on goal" means more chances to score, and the next attempt, by Houston-based Intuitive Machines, launches in February.
Astrobotic itself will get another chance in November with its Griffin lander transporting NASA's VIPER rover to the lunar south pole.
For now, the Pittsburgh-based company is staying tight-lipped on Peregrine's intended destination, leaving enthusiasts to make their own calculations.
Amateur astronomer Tony Dunn used publicly available data provided by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to plot out the spaceship's current course, posting a graphic on social media platform X showing it would collide with the Moon on January 23.
But "it's really anybody's guess as to what is actually going to happen because of the leaking fuel," which could easily push it off course, he told AFP.
Or, Astrobotic could intentionally point Peregrine another way, such as flying by the Moon and shooting for interplanetary space.
While a hard lunar landing might satisfy some of Astrobotic's clients, such as those flying human ashes and DNA to the Moon, it could anger others like the Navajo Nation, which had called that cargo a "desecration" of the celestial body.
"I think it would be a shame if they completed their failed mission by littering the surface of the Moon with debris," Justin Walsh, a professor of art history, archaeology, and space studies at USC told AFP, adding that humanity had left some 180 tons of material on the surface since the first Soviet impactor crashed in 1959.
Y.Jeong--CPN


