-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school

-
 Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
-
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle

-
 Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
-
Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote

-
 Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
-
UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall

-
 Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
-
New Zealand deputy PM defends claims colonisation good for Maori

-
 Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
-
Deadly storm sparks floods in Spain, raises calls to postpone Portugal vote

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
-
Lower pollution during Covid boosted methane: study

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
-
Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending

-
 Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
-
Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links

-
 ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
-
Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal

-
 ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
-
What does Iran want from talks with the US?

-
 Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
-
Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election

-
 Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
-
Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls

-
 Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
-
BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover

-
 UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
-
Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics

-
 Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
-
Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast

-
 Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
-
German factory orders rise at fastest rate in 2 years in December

-
 Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
-
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation

-
 Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment
Stocks in retreat as traders reconsider tech investment
-
Fiji football legend returns home to captain first pro club


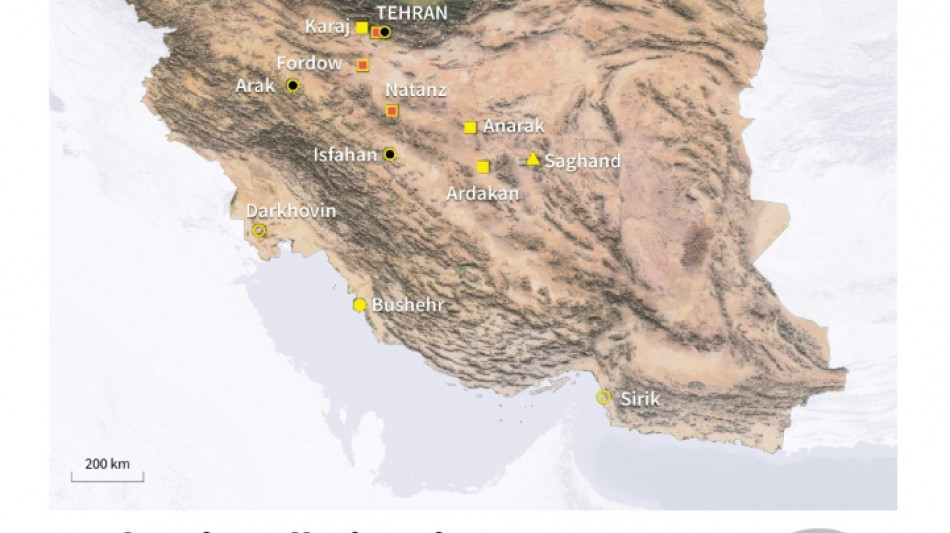
Iran's nuclear programme: the key sites
Before Israeli strikes on Friday, Washington and Tehran had held several rounds of talks on Iran's nuclear programme, as concerns mounted about its rapid expansion.
Iran has significantly ramped up its nuclear programme in recent years, after a landmark deal with world powers curbing its nuclear activities in exchange for sanction relief began to unravel in 2018 when the United States unilaterally withdrew.
As of mid-May, Iran's total enriched uranium stockpile was estimated at 9,247.6 kilograms -- or more than 45 times the limit set out in the 2015 deal -- according to the latest report by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA).
Among its stockpiles, Iran has an estimated 408.6 kilograms enriched to up to 60 percent -- just a short step from the 90 percent needed for a nuclear warhead.
The country now theoretically has enough near-weapons-grade material, if further refined, for about 10 nuclear bombs, according to the definition by the Vienna-based IAEA.
But Iran has always denied any ambition to develop nuclear weapons.
Below is a list of Iran's key nuclear sites, which are subject to regular inspections by the UN nuclear watchdog:
- Uranium enrichment plants -
Natanz
About 250 kilometres (150 miles) south of Tehran, Natanz is Iran's heavily bunkered main uranium enrichment site, whose existence was first revealed in 2002.
Natanz operates nearly 70 cascades of centrifuges at its two enrichment plants, one of which is underground. A cascade is a series of centrifuges -- machines used in the process of enriching uranium.
In April 2021, the site was damaged in an attack that Iran said was an act of sabotage by Israel.
On Friday, Israel's operation struck at the "heart of Iran's nuclear enrichment programme", targeting the atomic facility in Natanz and nuclear scientists, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said.
IAEA head Rafael Grossi confirmed the Natanz site was "among targets".
Fordo
Secretly built in violation of United Nations resolutions under a mountain near the holy central city of Qom, Fordo was first publicly revealed in 2009.
Initially described as an "emergency" facility built underground to protect it from potential air attacks, Iran later indicated it was an enrichment plant capable of housing about 3,000 centrifuges.
In 2023, uranium particles enriched up to 83.7 percent were discovered at the Fordo plant, which Iran claimed were the product of "unintended fluctuations" during the enrichment process.
- Uranium conversion and research reactors -
Isfahan
At the uranium conversion facility at Isfahan in central Iran, raw mined uranium is processed into uranium tetrafluoride (UF4) and then into uranium hexafluoride (UF6), a feed gas for centrifuges.
The plant was industrially tested in 2004 upon its completion.
The Isfahan centre also harbours a nuclear fuel fabrication facility, which was inaugurated in 2009 and produces low-enriched fuel for use in power plants.
In July 2022, Iran announced plans to construct a new research reactor there.
Arak
Work on the Arak heavy-water research reactor on the outskirts of the village of Khondab began in the 2000s, but was halted under the terms of the 2015 deal.
Iran has meanwhile informed the IAEA about its plans to commission the reactor by 2026.
The research reactor was officially intended to produce plutonium for medical research and the site includes a production plant for heavy water.
Tehran
The Tehran nuclear research centre houses a reactor that was supplied by the United States in 1967 for the production of medical radioisotopes.
- Nuclear power plant -
Bushehr
Iran's only nuclear power plant in the southern port city of Bushehr was built by Russia and began operating at a lower capacity in 2011 before being plugged into the national power grid in 2012.
Russia continues to deliver nuclear fuel for the plant, which remains under IAEA control.
A German company began construction on the plant with a 1,000-megawatt nominal capacity until the project was halted in the wake of the 1979 Islamic revolution. Moscow later completed it.
Darkhovin and Sirik
Iran began construction in late 2022 on a 300-megawatt power plant in Darkhovin, in the country's southwest. In early 2024, it also began work in Sirik, in the Strait of Hormuz, on a new complex of four individual plants with a combined capacity of 5,000 megawatts.
M.García--CPN
