
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain

-
 Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
-
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school

-
 Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
-
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle

-
 Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
-
Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote

-
 Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
-
UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall

-
 Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
-
New Zealand deputy PM defends claims colonisation good for Maori

-
 Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
-
Deadly storm sparks floods in Spain, raises calls to postpone Portugal vote

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
-
Lower pollution during Covid boosted methane: study

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
-
Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending

-
 Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
-
Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links

-
 ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
-
Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal

-
 ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
-
What does Iran want from talks with the US?

-
 Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
-
Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election

-
 Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
-
Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls

-
 Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
-
BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover

-
 UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
-
Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics

-
 Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
-
Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast

-
 Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
-
German factory orders rise at fastest rate in 2 years in December

-
 Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
-
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation


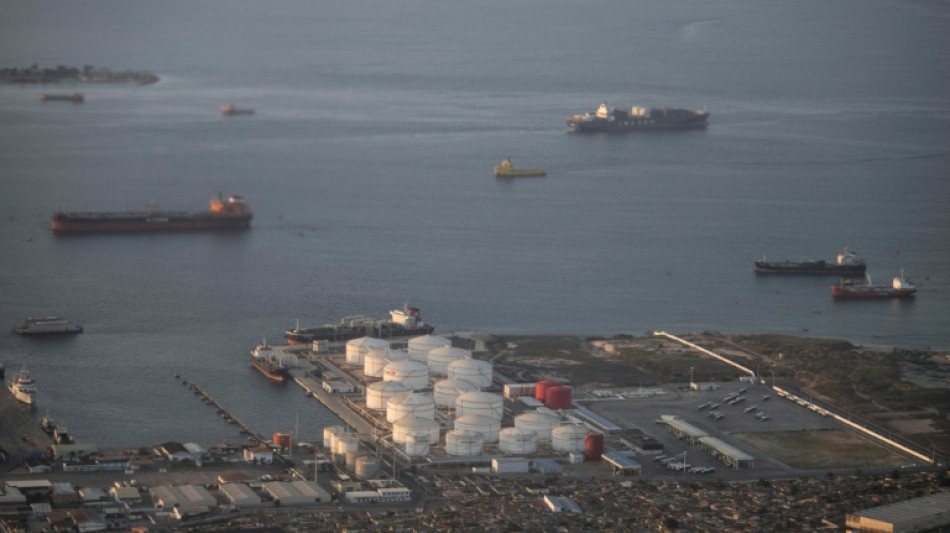
Oil under $65 a boon for consumers, but a burden on producers
US President Donald Trump's tariffs, his call to "drill baby drill" and especially a decision by OPEC+ to hike crude output quotas have oil prices trading at lows not seen since the Covid pandemic.
That is good news for consumers but not so much for producers, analysts say.
A barrel of Brent North Sea crude, the international benchmark, stands below $65, a far cry from the more than the $120 reached in 2022 following the invasion of Ukraine by major oil producer Russia.
- Lower inflation -
The fall in oil prices has contributed to a global slowdown for inflation, while also boosting growth in countries reliant on importing crude, such as much of Europe.
The US consumer price index, for example, was down 11.8 percent year-on-year in April.
Cheaper crude "increases the level of disposable income" consumers have to be spending on "discretionary items" such as leisure and tourism, said Pushpin Singh, an economist at British research group Cebr.
The price of Brent has fallen by more than $10 compared with a year ago, reducing the cost of various fuel types derived directly from oil.
This is helping to push down transportation and manufacturing costs that may, in the medium term, help further cut prices of consumer goods, Singh told AFP.
But he noted that while the drop in crude prices is partly a consequence of Trump's trade policies, the net effect on inflation remains difficult to predict amid threatened surges to other input costs, such as metals.
At the same time, "cheaper oil can make renewable energy sources less competitive, potentially slowing investment in green technologies", Singh added.
- Oil producers -
As prices retreat however the undisputed losers are oil-producing countries, "especially high-cost producers who at current and lower prices are forced to scale back production in the coming months", said Ole Hansen, head of commodity strategy at Saxo Bank.
Oil trading close to or below $60 "will obviously not be great for shale producers" either, said Rystad Energy analyst Jorge Leon.
"Having lower oil prices is going to be the detriment to their development," he told AFP.
Some companies extracting oil and natural gas from shale rock have already announced reduced investment in the Permian Basin, located between Texas and New Mexico.
For the OPEC+ oil alliance, led by Saudi Arabia and Russia, tolerance for low prices varies greatly.
Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Kuwait have monetary reserves allowing them to easily borrow to finance diversified economic projects, Leon said.
Hansen forecast that "the long-term winners are likely to be major OPEC+ producers, especially in the Middle East, as they reclaim market shares that were lost since 2022 when they embarked on voluntary production cuts".
The 22-nation group began a series of cuts in 2022 to prop up crude prices, but Saudi Arabia, Russia and six other members surprised markets recently by sharply raising output.
On Saturday, the countries announced a huge increase in crude production for July with an additional 411,000 barrels a day.
Analysts say the hikes have likely been aimed at punishing OPEC members that have failed to meet their quotas, but it also follows pressure from Trump to lower prices.
That is directly impacting the likes of Iran and Venezuela, whose economies depend heavily on oil revenues.
A lower-price environment also hurts Nigeria, which like other OPEC+ members possesses a more limited ability to borrow funds, according to experts.
Bit non-OPEC member Guyana, whose GDP growth has surged in recent years thanks to the discovery of oil, risks seeing its economy slow.
J.Bondarev--CPN
