
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
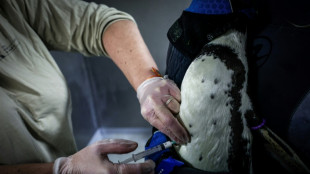
Penguins queue in Paris zoo for their bird flu jabs
-
 Sri Lanka issues fresh landslide warnings as toll nears 500
Sri Lanka issues fresh landslide warnings as toll nears 500
-
Stocks, dollar rise before key US inflation data

-
 After wins abroad, Syria leader must gain trust at home
After wins abroad, Syria leader must gain trust at home
-
Markets rise ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut

-
 German factory orders rise more than expected
German factory orders rise more than expected
-
Flooding kills two as Vietnam hit by dozens of landslides

-
 Italy to open Europe's first marine sanctuary for dolphins
Italy to open Europe's first marine sanctuary for dolphins
-
Hong Kong university suspends student union after calls for fire justice

-
 Asian markets rise ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut
Asian markets rise ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut
-
Georgia's street dogs stir affection, fear, national debate

-
 Pandas and ping-pong: Macron ending China visit on lighter note
Pandas and ping-pong: Macron ending China visit on lighter note
-
TikTok to comply with 'upsetting' Australian under-16 ban

-
 Pentagon endorses Australia submarine pact
Pentagon endorses Australia submarine pact
-
Softbank's Son says super AI could make humans like fish, win Nobel Prize

-
 OpenAI strikes deal on US$4.6 bn AI centre in Australia
OpenAI strikes deal on US$4.6 bn AI centre in Australia
-
Rains hamper Sri Lanka cleanup after deadly floods

-
 Unchecked mining waste taints DR Congo communities
Unchecked mining waste taints DR Congo communities
-
Asian markets mixed ahead of US data, expected Fed rate cut

-
 French almond makers revive traditions to counter US dominance
French almond makers revive traditions to counter US dominance
-
Aid cuts causing 'tragic' rise in child deaths, Bill Gates tells AFP

-
 Abortion in Afghanistan: 'My mother crushed my stomach with a stone'
Abortion in Afghanistan: 'My mother crushed my stomach with a stone'
-
Mixed day for US equities as Japan's Nikkei rallies

-
 To counter climate denial, UN scientists must be 'clear' about human role: IPCC chief
To counter climate denial, UN scientists must be 'clear' about human role: IPCC chief
-
Facebook 'supreme court' admits 'frustrations' in 5 years of work

-
 South Africa says wants equal treatment, after US G20 exclusion
South Africa says wants equal treatment, after US G20 exclusion
-
One in three French Muslims say suffer discrimination: report
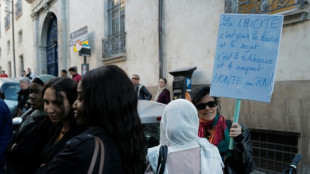
-
 Microsoft faces complaint in EU over Israeli surveillance data
Microsoft faces complaint in EU over Israeli surveillance data
-
Milan-Cortina organisers rush to ready venues as Olympic flame arrives in Italy

-
 Truth commission urges Finland to rectify Sami injustices
Truth commission urges Finland to rectify Sami injustices
-
Stocks rise eyeing series of US rate cuts

-
 Italy sweatshop probe snares more luxury brands
Italy sweatshop probe snares more luxury brands
-
EU hits Meta with antitrust probe over WhatsApp AI features

-
 Russia's Putin heads to India for defence, trade talks
Russia's Putin heads to India for defence, trade talks
-
South Africa telecoms giant Vodacom to take control of Kenya's Safaricom

-
 Markets mixed as traders struggle to hold Fed cut rally
Markets mixed as traders struggle to hold Fed cut rally
-
Asian markets mixed as traders struggle to hold Fed cut rally

-
 In Turkey, ancient carved faces shed new light on Neolithic society
In Turkey, ancient carved faces shed new light on Neolithic society
-
Asian markets stumble as traders struggle to hold Fed cut rally

-
 Nintendo launches long-awaited 'Metroid Prime 4' sci-fi blaster
Nintendo launches long-awaited 'Metroid Prime 4' sci-fi blaster
-
Trump scraps Biden's fuel-economy standards, sparking climate outcry

-
 US stocks rise as weak jobs data boosts rate cut odds
US stocks rise as weak jobs data boosts rate cut odds
-
Poor hiring data points to US economic weakness

-
 Germany to host 2029 women's Euros
Germany to host 2029 women's Euros
-
Satellite surge threatens space telescopes, astronomers warn

-
 Greek govt warns farmers not to escalate subsidy protest
Greek govt warns farmers not to escalate subsidy protest
-
EU agrees deal to ban Russian gas by end of 2027

-
 Former king's memoirs hits bookstores in Spain
Former king's memoirs hits bookstores in Spain
-
German lithium project moves ahead in boost for Europe's EV sector


Every heatwave enhanced by climate change: experts
All heatwaves today bear the unmistakable and measurable fingerprint of global warming, top experts on quantifying the impact of climate change on extreme weather said Wednesday.
Burning fossil fuels and destroying forests have released enough greenhouse gases into the atmosphere to also boost the frequency and intensity of many floods, droughts, wildfires and tropical storms, they detailed in a state-of-science report.
"There is no doubt that climate change is a huge game changer when it comes to extreme heat," Friederike Otto, a scientist at Imperial College London's Grantham Institute, told AFP.
Extreme hot spells such as the heatwave that gripped South Asia in March and April are already the most deadly of extreme events, she added.
"Every heatwave in the world is now made stronger and more likely to happen because of human-caused climate change," Otto and co-author Ben Clarke of the University of Oxford said in the report, presented as a briefing paper for the news media.
Evidence of global warming's impact on extreme weather has been mounting for decades, but only recently has it been possible to answer the most obvious of questions: To what extent was a particular event caused by climate change?
The most scientists could say before is that an unusually severe hurricane, flood or heatwave was consistent with general predictions of how global warming would eventually influence weather.
News media, meanwhile, sometimes left climate change out of the picture altogether or, at the other extreme, mistakenly attributed a weather disaster entirely to rising temperatures.
With more data and better tools, however, Otto and other pioneers of a field known as event attribution science have been able to calculate -- sometimes in near realtime -- how much more likely or intense a particular storm or hot spell has become due to global warming.
- Courtroom evidence -
Otto and colleagues in the World Weather Attribution (WWA) consortium, for example, concluded that the heatwave that gripped western North America last June -- sending temperatures in Canada to a record 49.6 C (121 F) -- would have been "virtually impossible" without human-induced climate change.
A heatwave that scorched India and Pakistan last month is still under review, Otto told AFP, but the larger picture is frighteningly clear.
"What we see right now in terms of extreme heat will be very normal, if not cool, in a 2-degree to 3-degree Celsius world," she said, referring to average global temperatures above preindustrial levels.
The world has warmed nearly 1.2C so far.
That increase made record-setting rainfall and flooding last July in Germany and Belgium that left more than 200 dead up to nine times more likely, the WWA found.
But global warming is not always to blame.
A two-year drought in southern Madagascar leading to near famine conditions attributed by the UN to climate change was in fact a product of natural variability in the weather, experts reported.
Quantifying the impact of global warming on extreme weather events using peer-reviewed methods has real-world policy implications.
Attribution studies, for example, have been used as evidence in landmark climate litigation in the United States, Australia and Europe.
In one case set to resume later this month, Saul Luciano Lliuya v. RWE AG, a Peruvian farmer is suing the German energy giant for the costs of preventing harmful flooding from a glacial lake destabilised by climate change.
A scientific assessment entered into evidence concluded that human-caused global warming is directly responsible for creating a "critical threat" of a devastating outburst, putting a city of some 120,000 people in the path of potential floodwaters.
Y.Uduike--CPN
