-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
'GOAT' battles to top of N. America box office

-
 Six stand-out moments from the 2026 Winter Olympics
Six stand-out moments from the 2026 Winter Olympics
-
St Francis relics go on public show for first time in Italy

-
 Brazil's Lula urges Trump to treat all countries equally
Brazil's Lula urges Trump to treat all countries equally
-
Copper, a coveted metal boosting miners

-
 AI agent invasion has people trying to pick winners
AI agent invasion has people trying to pick winners
-
Cuban Americans keep sending help to the island, but some cry foul

-
 Klaebo makes Olympic history as Gu forced to wait
Klaebo makes Olympic history as Gu forced to wait
-
NASA chief rules out March launch of Moon mission over technical issues

-
 AI revolution looms over Berlin film fest
AI revolution looms over Berlin film fest
-
Libya's Ramadan celebrations tempered by economic woes

-
 French volunteer bakes for Ukraine amid frosts and power outages
French volunteer bakes for Ukraine amid frosts and power outages
-
Gu shoots for elusive gold as Klaebo makes Olympic history

-
 Global summit calls for 'secure, trustworthy and robust AI'
Global summit calls for 'secure, trustworthy and robust AI'
-
Trump, once unstoppable, hits snag after snag ahead of major US address

-
 Tomb more than 1,000 years old found in Panama
Tomb more than 1,000 years old found in Panama
-
Battered by Gaza war, Israel's tech sector in recovery mode

-
 'Not the end': Small US firms wary but hopeful on tariff upheaval
'Not the end': Small US firms wary but hopeful on tariff upheaval
-
UK govt considers removing ex-prince Andrew from line of succession

-
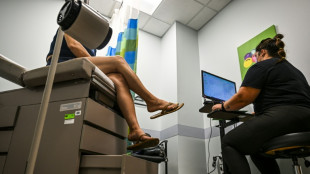 New study probes why chronic pain lasts longer in women
New study probes why chronic pain lasts longer in women
-
Counting the cost: Minnesota reels after anti-migrant 'occupation'

-
 Stocks rise after court ruling against US tariffs
Stocks rise after court ruling against US tariffs
-
German broadcaster recalls correspondent over AI-generated images

-
 US Supreme Court strikes down swath of Trump global tariffs
US Supreme Court strikes down swath of Trump global tariffs
-
Stocks volatile after soft US growth data, court ruling against tariffs

-
 US GDP growth misses expectations as Trump blames shutdown
US GDP growth misses expectations as Trump blames shutdown
-
European stocks rebound, oil prices ease after US-Iran volatility

-
 India chases 'DeepSeek moment' with homegrown AI
India chases 'DeepSeek moment' with homegrown AI
-
Florida airport to be renamed after US President Donald Trump

-
 Stocks mixed, oil rises after Trump Iran threat
Stocks mixed, oil rises after Trump Iran threat
-
Victorious Takaichi promises 'strong and prosperous' Japan

-
 Nvidia nears deal for scaled-down investment in OpenAI: report
Nvidia nears deal for scaled-down investment in OpenAI: report
-
Japan inflation eases in welcome news for PM Takaichi

-
 Stocks drop, oil rises after Trump Iran threat
Stocks drop, oil rises after Trump Iran threat
-
India chases 'DeepSeek moment' with homegrown AI models

-
 World leaders to declare shared stance on AI at India summit
World leaders to declare shared stance on AI at India summit
-
NASA delivers harsh assessment of botched Boeing Starliner test flight

-
 UK king opens London fashion week despite brother's arrest
UK king opens London fashion week despite brother's arrest
-
Striking Argentine workers slow down Buenos Aires in protest over labor reforms

-
 Rocket re-entry pollution measured in atmosphere for first time
Rocket re-entry pollution measured in atmosphere for first time
-
US threatens to leave IEA if net zero focus remains

-
 Walmart outlines big AI ambitions as it reports mixed results
Walmart outlines big AI ambitions as it reports mixed results
-
British public cheer Andrew's arrest with a smile and relief

-
 What we know about ex-prince Andrew's friendship with Epstein
What we know about ex-prince Andrew's friendship with Epstein
-
Oil extends gains on US-Iran tensions, stocks retreat

-
 UK police arrest ex-prince Andrew on suspicion of misconduct
UK police arrest ex-prince Andrew on suspicion of misconduct
-
Oil extends gains on US-Iran tensions, Europe stocks slide

-
 Former prince Andrew, a historic downfall
Former prince Andrew, a historic downfall
-
OpenAI's Altman tells leaders regulation 'urgently' needed

U.S. Jobs stall, gdp slows
The phrase “the economy is suffocating” is the sort of provocation normally reserved for campaign platforms and market panic. Yet the latest hard numbers offer a more unsettling reality: not a dramatic plunge, but a steady constriction—growth that is still positive, but markedly weaker; job creation that continues, but increasingly narrow; and a labour market whose stress is showing up less in flashy headlines than in the quiet arithmetic of participation, long-term unemployment, and where the jobs are actually being created.
A recent widely circulated economic video framed the moment as an economy running short of oxygen—employment “collapsing” while output slows. The language is blunt; the underlying diagnosis is harder to dismiss. The newest official releases describe an economy that is not in freefall, but is plainly losing momentum and breadth. The risk is not merely slower growth; it is the kind of slowdown that changes behaviour—when employers delay hiring, households postpone big purchases, and confidence erodes long before the data formally declares a downturn.
Growth is still growth—until it isn’t
The advance estimate for output in the final quarter of 2025 delivered a sharp deceleration. Real GDP expanded at an annual rate of 1.4% in Q4 2025, down from 4.4% in Q3 2025. The economy, in other words, did not contract; it slowed—dramatically. That distinction matters, but so does the direction of travel. A drop of roughly three percentage points in the growth rate over a single quarter is not statistical noise; it is a meaningful loss of speed.
This matters because headline GDP is not merely a retrospective scorecard. It shapes expectations—about profits, wages, tax receipts, and the room policymakers have to manoeuvre. When growth cools this quickly, the question is no longer whether the economy can keep expanding; it is what must happen for it to re-accelerate, and whether those conditions are present.
Slower GDP growth also changes the “feel” of the economy even when employment remains positive. Households experience it as fewer hours, fewer opportunities to switch jobs for better pay, and a rising sense that prices and borrowing costs are harder to outrun. Businesses experience it as cautious demand, more price sensitivity, and a higher bar for investment.
Employment: the headline number hides the squeeze
The labour market’s newest monthly snapshot carries an apparent contradiction. On the surface, payrolls rose by 130,000 in January, a respectable gain by pre-pandemic standards. Beneath the surface, the more telling line is what came next: in 2025, payroll employment “changed little,” averaging only about 15,000 jobs per month. That is not a vibrant labour market; it is a near-stall—an economy still creating jobs, but only just.
The pattern of January’s hiring sharpens the point. The gains were heavily concentrated:
- Health care added 82,000 jobs.
- Social assistance rose by 42,000.
- Construction added 33,000.
Together, those three categories total 157,000—more than the entire headline increase of 130,000. The implication is straightforward: outside those pockets, the rest of the economy collectively shed around 27,000 jobs on net. This is the anatomy of a late-cycle labour market: hiring that persists, but in sectors that are either structurally supported (health care demand driven by demographics and backlogs) or buffered by ongoing projects and contracts (construction), while many other industries hover near flat, or quietly contract.
A labour market that is “working” can still be weakening
The unemployment rate is not at crisis levels. Yet it is drifting higher than the unusually low rates of the earlier post-pandemic expansion, and the composition of unemployment is becoming more concerning. Long-term unemployment—people out of work for 27 weeks or more—stood at 1.8 million in January, accounting for one quarter of all unemployed people. More strikingly, the long-term unemployed count is up by 386,000 from a year earlier. That is a classic indicator of a labour market that is tightening its grip: when hiring slows, jobless spells lengthen, and the pathway back into work becomes steeper. At the same time, the labour force participation rate remained around 62.5%, with the employment-population ratio at 59.8%—figures that suggest limited progress in drawing more people into work. If job growth is slowing while participation is steady, the economy can absorb shocks less easily. A weaker quarter of hiring, a pullback in investment, or a reduction in public-sector employment can then translate into a faster rise in unemployment.
A further sign of pressure appears among those on the margins of the labour force. The number of people not in the labour force who still want a job fell to 5.8 million, a sizeable decline from the previous month. That drop can be read in two ways. Optimistically, it could mean fewer people want work because more have found it. Less optimistically, it can reflect discouragement—people who want employment, but see too few viable opportunities to keep searching actively enough to be counted as unemployed.
Meanwhile, the number of marginally attached workers—those who want work, are available, and have looked in the last year, but not in the most recent month—stood at 1.7 million, including 475,000 discouraged workers. These are not fringe statistics; they are the shadow edge of the labour market, where strain appears earlier than in headline payrolls.
Where the jobs are—and where they are disappearing
In a broad-based expansion, employment gains are distributed across industries: goods and services, cyclical and defensive sectors, private and public. That is not the pattern now. Health care remains the engine of job growth, and it is not subtle. It added 82,000 jobs in January alone, with gains in ambulatory services, hospitals, and nursing and residential care facilities. These are vital jobs—but they are not, by themselves, a signal that the private economy is surging. They speak to an underlying demand for care, not necessarily rising discretionary spending or business investment.
Construction’s gain of 33,000 suggests ongoing activity, but the same report notes that construction employment was essentially flat over 2025 as a whole. That is consistent with a sector that can post strong months but is not in a sustained upswing. Perhaps most politically and economically sensitive is what is happening in government payrolls. Federal government employment fell by 34,000 in January, continuing a broader decline linked to earlier workforce changes. Since a peak in October 2024, federal employment is down by 327,000, a drop of 10.9%. Regardless of one’s view of public-sector size, a reduction of that scale is large enough to ripple through local economies, contracting, and household spending in affected regions.
Financial activities are also under pressure. The sector lost 22,000 jobs in January and is down 49,000 since a recent peak in May 2025. A shrinking financial sector can be both a symptom and a cause of slower growth: it reflects weaker deal flow and lending activity, and it can reinforce tightening conditions as firms reduce capacity and risk appetite. Beyond these moves, many major industries showed little change. That “quiet” is itself a signal. When the labour market is humming, “little change” across many sectors would be unusual. In a cooling economy, it becomes the norm.
Wages are rising—but that does not mean households feel relief
Average hourly earnings increased 0.4% in January to $37.17, putting year-on-year wage growth at 3.7%. For production and non-supervisory workers, earnings also rose 0.4%, to $31.95. Steady wage growth can be a sign of resilience. But it can also coexist with an increasingly anxious labour market. When job switching slows, wage gains are more likely to be incremental rather than transformational. Workers may see pay rising, but feel less able to negotiate, less willing to take risks, and more concerned about job security. In practical terms, an economy can “suffocate” not because wages collapse, but because the combination of slower hiring, slower output growth, and elevated costs squeezes households from multiple angles at once: fewer opportunities to move up, less confidence in future income, and higher sensitivity to shocks.
The GDP slowdown and the labour stall are reinforcing each other
GDP and employment are intertwined, but they are not the same. Output can slow while jobs still rise, particularly if productivity changes, if hiring lags the cycle, or if growth is supported by a narrow band of sectors. But the current combination—sharp GDP deceleration and a labour market that barely expanded through 2025—creates an uncomfortable feedback loop.
When GDP slows, businesses become cautious. When businesses become cautious, hiring slows. When hiring slows, consumer confidence weakens. When confidence weakens, spending and investment soften further. This is how expansions age—not with a single catastrophic event, but with an accumulation of small “no’s”: no new hires, no new factories, no major purchases, no expansions into new markets. The economy can stay in that state for some time. But it becomes fragile. In a fragile state, the difference between “slow growth” and “recession” is often a short list of triggers: a credit shock, an external disruption, a sharp fall in business confidence, or policy uncertainty that prompts firms to protect cash rather than pursue growth.
Why dramatic language resonates now
Calling the economy “suffocating” is emotive, and official statistics rarely oblige the drama. Yet the phrase captures something real: the sensation of constraint. An economy does not need to be shrinking for people to feel worse off. It only needs to be less forgiving—less able to offer second chances, wage upgrades, or quick re-employment.
The latest data points towards an economy in which job creation is not broad, long-term unemployment is rising, and output growth is cooling quickly. That combination can be experienced as a squeeze even if the top-line numbers remain positive. It also explains why narratives of “collapse” gain traction. When the labour market is dominated by a few sectors and the rest is flat to negative, many communities and occupations will indeed experience something that feels like collapse—hiring freezes, rescinded offers, and fewer pathways forward. National averages can conceal that unevenness for months.
What to watch next
If the question is whether the economy is “suffocating,” the answer will be decided by breadth and persistence—whether weakness spreads beyond isolated pockets, and whether the slowdown in growth proves temporary or entrenched.
The most important signals in the months ahead will include:
- Whether job gains broaden beyond health care and social assistance.
- Whether long-term unemployment continues to rise as a share of total unemployment.
- Whether participation improves—or whether more would-be workers drift into the margins.
- Whether GDP growth stabilises or weakens further after the Q4 deceleration.
- Whether job losses in interest-sensitive and confidence-sensitive areas (such as finance) extend into other parts of the private economy.
For now, the evidence does not describe an economy that has stopped breathing. It describes one that is breathing more shallowly—still moving forward, but with less air in its lungs, and less margin for error. That is precisely the point at which small shocks become large stories, and when the rhetoric of “suffocation” stops sounding like hyperbole and starts sounding like a warning.

Nicaragua on the brink?

Cuba: The Regime's last Card

Strike fears rise over Iran

Japan’s right‑turn triumph

EU India deal gains unveiled

AI sparks Wall Street panic

India defies U.S. tariffs

EU misstep on mercosur Deal

Argentina reshapes oil

Power at the Heart of Iran

Cuba Strangled by US Pressure




