-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount

-
 Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
-
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal

-
 Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
-
ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future

-
 EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
-
Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom

-
 Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
-
CNN's future unclear as Trump applies pressure

-
 German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases
German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases
-
EU's Mercosur trade deal hits French, Italian roadblock

-
 Warner Bros rejects Paramount bid, sticks with Netflix
Warner Bros rejects Paramount bid, sticks with Netflix
-
Crude prices surge after Trump orders Venezuela oil blockade

-
 Warner Bros. Discovery rejects Paramount bid
Warner Bros. Discovery rejects Paramount bid
-
Doctors in England go on strike for 14th time

-
 Ghana's Highlife finds its rhythm on UNESCO world stage
Ghana's Highlife finds its rhythm on UNESCO world stage
-
Stocks gain as traders bet on interest rate moves

-
 France probes 'foreign interference' after malware found on ferry
France probes 'foreign interference' after malware found on ferry
-
Europe's Ariane 6 rocket puts EU navigation satellites in orbit

-
 Bleak end to the year as German business morale drops
Bleak end to the year as German business morale drops
-
Hundreds queue at Louvre museum as strike vote delays opening

-
 Markets rise even as US jobs data fail to boost rate cut bets
Markets rise even as US jobs data fail to boost rate cut bets
-
Asian markets mixed as US jobs data fails to boost rate cut hopes

-
 Bondi shooting shocks, angers Australia Jewish community
Bondi shooting shocks, angers Australia Jewish community
-
UK experiences sunniest year on record

-
 Australia holds first funerals for Bondi Beach attack victims
Australia holds first funerals for Bondi Beach attack victims
-
Netflix boss promises Warner Bros films would still be seen in cinemas

-
 Tepid 2026 outlook dents Pfizer shares
Tepid 2026 outlook dents Pfizer shares
-
EU weakens 2035 combustion-engine ban to boost car industry

-
 Arctic sees unprecedented heat as climate impacts cascade
Arctic sees unprecedented heat as climate impacts cascade
-
VW stops production at German site for first time


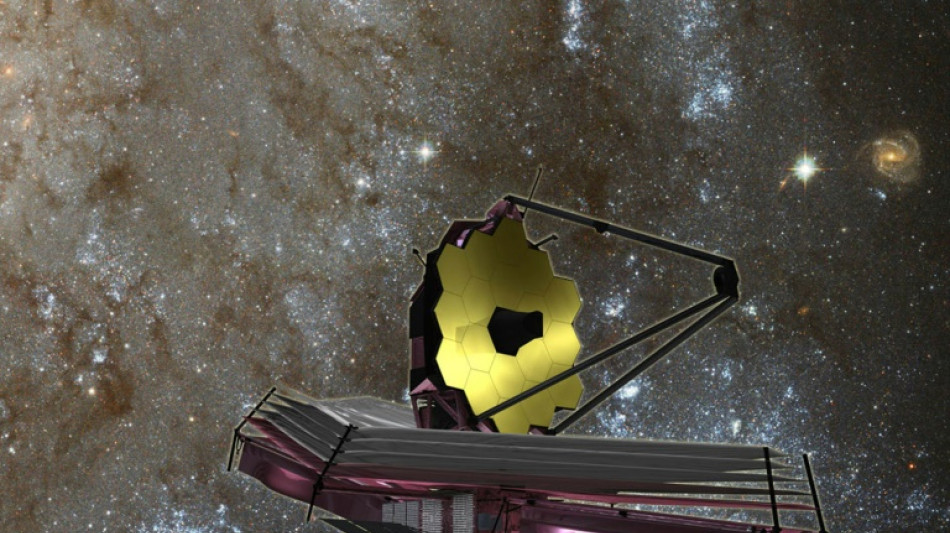
Webb spots surprisingly massive galaxies in early universe
The James Webb Space Telescope has spotted six massive galaxies that emerged not long after the Big Bang, a study said Wednesday, surprising scientists by forming at a speed that contradicts our current understanding of the universe.
Since becoming operational last July, the Webb telescope has been peering farther than ever before into the universe's distant reaches -- which also means it is looking back in time.
For its latest discovery, the telescope spied galaxies from between 500 to 700 years million years after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago, meaning the universe was under five percent of its current age.
Webb's NIRCam instrument, which operates in the near infrared wavelength invisible to the naked eye, observed the six galaxies in a little-known region of the sky, according to a study published in the journal Nature.
Two of the galaxies had previously been spotted by the Hubble Space Telescope but were so faint in those images that they went unnoticed.
These six new "candidate galaxies", so-called because their discovery still needs to be confirmed by other measurements, contain many more stars than scientists expected.
One galaxy is even believed to have around 100 billion stars.
That would make it around the size of the Milky Way, which is "crazy," the study's first author Ivo Labbe told AFP.
- 'Off a cliff' -
It took our home galaxy the entire life of the universe for all its stars to assemble.
For this young galaxy to achieve the same growth in just 700 million years, it would have had to grow around 20 times faster than the Milky Way, said Labbe, a researcher at Australia's Swinburne University of Technology.
For there to be such massive galaxies so soon after the Big Bang goes against the current cosmological model which represents science's best understanding of how the universe works.
"According to theory, galaxies grow slowly from very small beginnings at early times," Labbe said, adding that such galaxies were expected to be between 10 to 100 times smaller.
But the size of these galaxies "really go off a cliff," he said.
What could be going on? One suspect is mysterious dark matter, which makes up a sizeable amount of the Universe.
While much about dark matter remains unknown, scientists believe it plays a key role in the formation of galaxies.
When dark matter "clumps" together into a halo, it attracts gas from the surrounding universe which in turn forms a galaxy and its stars, Labbe said.
But this process is supposed to take a long time, and "in the early universe, there's just not that many clumps of dark matter," he said.
- 'Model is cracking' -
The newly discovered galaxies could indicate that things sped up far faster in the early universe than previously thought, allowing stars to form "much more efficiently," said David Elbaz, an astrophysicist at the French Atomic Energy Commission not involved in the research.
This could be linked to recent signs that the universe itself is expanding faster than we once believed, he added.
This subject sparks fierce debate among cosmologists, making this latest discovery "all the more exciting, because it is one more indication that the model is cracking," Elbaz said.
Elbaz is one of many scientists working on the European Space Agency's Euclid space telescope, which is scheduled to launch in July to join Webb in space.
Euclid's mission is to uncover the secrets of dark matter and dark energy -- and it could also help solve this latest mystery, Elbaz said.
Labbe referred to the "black swan theory", under which just one unexpected event can overturn our previous understanding -- such as when Europeans saw the first black swans in Australia.
He called the galaxies "six black swans -- if even one of them turns out to be true, then it means we have to change our theories."
M.Anderson--CPN


