
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
BP profits slide awaiting new CEO

-
 Trump tariffs hurt French wine and spirits exports
Trump tariffs hurt French wine and spirits exports
-
OpenAI starts testing ads in ChatGPT

-
 Back to black: Philips posts first annual profit since 2021
Back to black: Philips posts first annual profit since 2021
-
Man arrested in Thailand for smuggling rhino horn inside meat

-
 'Family and intimacy under pressure' at Berlin film festival
'Family and intimacy under pressure' at Berlin film festival
-
Asian markets extend gains as Tokyo enjoys another record day

-
 Unions rip American Airlines CEO on performance
Unions rip American Airlines CEO on performance
-
Jury told that Meta, Google 'engineered addiction' at landmark US trial

-
 Three missing employees of Canadian miner found dead in Mexico
Three missing employees of Canadian miner found dead in Mexico
-
Meta, Google face jury in landmark US addiction trial

-
 Epstein accomplice Maxwell seeks Trump clemency before testimony
Epstein accomplice Maxwell seeks Trump clemency before testimony
-
Some striking NY nurses reach deal with employers

-
 Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure
Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure
-
EU chief backs Made-in-Europe push for 'strategic' sectors

-
 AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
-
Iran steps up arrests while remaining positive on US talks

-
 Bank of France governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau to step down in June
Bank of France governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau to step down in June
-
EU warns Meta it must open up WhatsApp to rival AI chatbots

-
 Japan restarts world's biggest nuclear plant again
Japan restarts world's biggest nuclear plant again
-
Japan's Takaichi may struggle to soothe voters and markets

-
 'Want to go home': Indonesian crew abandoned off Africa demand wages
'Want to go home': Indonesian crew abandoned off Africa demand wages
-
Arguments to begin in key US social media addiction trial

-
 Trump says China's Xi to visit US 'toward the end of the year'
Trump says China's Xi to visit US 'toward the end of the year'
-
'Send Help' repeats as N.America box office champ

-
 US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space
US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space
-
UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy

-
 Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off
Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off
-
French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping

-
 De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
-
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?

-
 Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
-
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya

-
 Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
-
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain

-
 Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
-
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school

-
 Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
-
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle


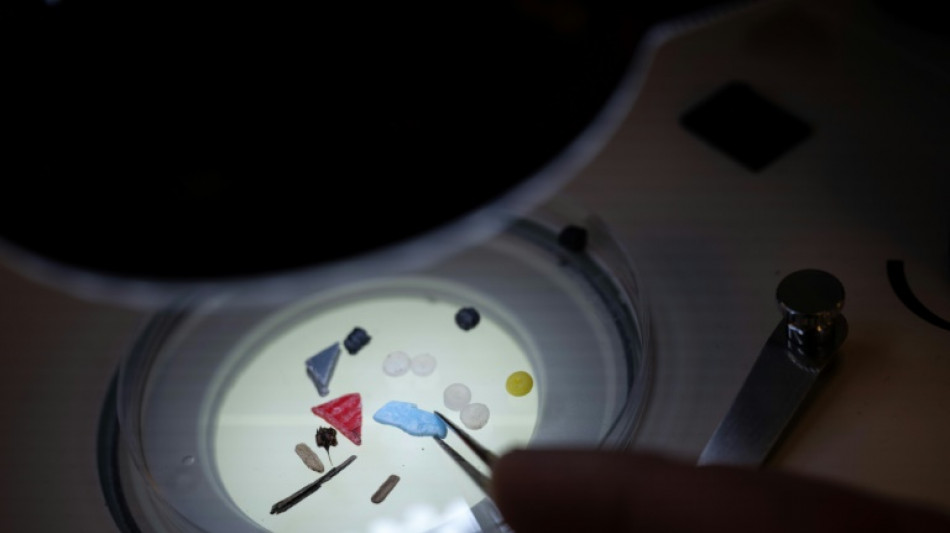
'Alarming' microplastic pollution in Europe's great rivers
"Alarming" levels of microplastic have been found in major rivers across Europe according to scientists in 14 studies published simultaneously Monday.
"The pollution is present in all European rivers" studied, said French scientist Jean-François Ghiglione, who coordinated the large-scale operation across nine major rivers from the Thames to the Tiber.
"Alarming" pollution of on average "three microplastics per cubic metre of water" was observed in all of them, according to the results published in the journal of Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
This is far from the 40 microplastics per cubic metre recorded in the world's 10 most polluted rivers -- the Yellow River, Yangtze, Mekong, Ganges, Nile, Niger, Indus, Amur, Pearl and Hai -- which irrigate countries where most plastic is produced or plastic waste is processed.
But this does not take into account the volume of water flowing.
- 3,000 particles per second -
On the Rhone in Valence, France, the fast flow means there are "3,000 plastic particles every second", said Ghiglione. The Seine in Paris has around 900 per second.
"The mass of microplastics invisible to the naked eye is more significant than that of the visible ones," said Ghiglione -- a result that "surprised" researchers. This was confirmed by analytical advances made during the studies, which began in 2019.
"Large microplastics float and are collected at the surface, while invisible ones are distributed throughout the water column and are ingested by many animals and organisms," said Ghiglione, head of research in marine microbial ecotoxicology at the French National Centre for Scientific Research (CNRS).
Samples were collected from the mouths of the rivers Elbe, Ebro, Garonne, Loire, Rhone, Rhine, Seine, Thames and the Tiber by some 40 chemists, biologists and physicists from 19 research laboratories.
The researchers then made their way upstream until they reached the first major city on each of the waterways.
"Microplastics are smaller than a grain of rice," said Alexandra Ter Halle, a chemist at the CNRS in Toulouse, who took part in the analysis.
- 'Mermaid tears' -
The particles are less than five millimetres in size, with the smallest invisible to the naked eye.
These include synthetic textile fibres from washing clothes and microplastics released from car tyres or when unscrewing plastic bottle caps.
Researchers also found virgin plastic pellets, the raw granules used to manufacture plastic products.
One of the studies identified a virulent bacterium on a microplastic in the Loire in France, capable of causing infections in humans.
Another unexpected finding was that a quarter of microplastics discovered in rivers are not derived from waste but come from industrial plastic pellets.
These granules, dubbed "mermaid tears", can also sometimes be found scattered along beaches after maritime incidents.
"What we see is the pollution is diffuse and established" and "comes from everywhere" in the rivers, he added.
"The international scientific coalition we are part of (as part of international UN negotiations on reducing plastic pollution) is calling for a major reduction in the production of primary plastic because we know that plastic production is directly linked to pollution," he said.
A.Leibowitz--CPN

