-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Spotify says active users up 11 percent in fourth quarter to 751 mn

-
 AstraZeneca profit jumps as cancer drug sales grow
AstraZeneca profit jumps as cancer drug sales grow
-
BP profits slide awaiting new CEO

-
 Trump tariffs hurt French wine and spirits exports
Trump tariffs hurt French wine and spirits exports
-
OpenAI starts testing ads in ChatGPT

-
 Back to black: Philips posts first annual profit since 2021
Back to black: Philips posts first annual profit since 2021
-
Man arrested in Thailand for smuggling rhino horn inside meat

-
 'Family and intimacy under pressure' at Berlin film festival
'Family and intimacy under pressure' at Berlin film festival
-
Asian markets extend gains as Tokyo enjoys another record day

-
 Unions rip American Airlines CEO on performance
Unions rip American Airlines CEO on performance
-
Jury told that Meta, Google 'engineered addiction' at landmark US trial

-
 Three missing employees of Canadian miner found dead in Mexico
Three missing employees of Canadian miner found dead in Mexico
-
Meta, Google face jury in landmark US addiction trial

-
 Epstein accomplice Maxwell seeks Trump clemency before testimony
Epstein accomplice Maxwell seeks Trump clemency before testimony
-
Some striking NY nurses reach deal with employers

-
 Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure
Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure
-
EU chief backs Made-in-Europe push for 'strategic' sectors

-
 AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
-
Iran steps up arrests while remaining positive on US talks

-
 Bank of France governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau to step down in June
Bank of France governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau to step down in June
-
EU warns Meta it must open up WhatsApp to rival AI chatbots

-
 Japan restarts world's biggest nuclear plant again
Japan restarts world's biggest nuclear plant again
-
Japan's Takaichi may struggle to soothe voters and markets

-
 'Want to go home': Indonesian crew abandoned off Africa demand wages
'Want to go home': Indonesian crew abandoned off Africa demand wages
-
Arguments to begin in key US social media addiction trial

-
 Trump says China's Xi to visit US 'toward the end of the year'
Trump says China's Xi to visit US 'toward the end of the year'
-
'Send Help' repeats as N.America box office champ

-
 US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space
US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space
-
UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy

-
 Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off
Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off
-
French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping

-
 De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums
-
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?

-
 Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents
-
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya

-
 Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks
-
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain

-
 Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
-
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school


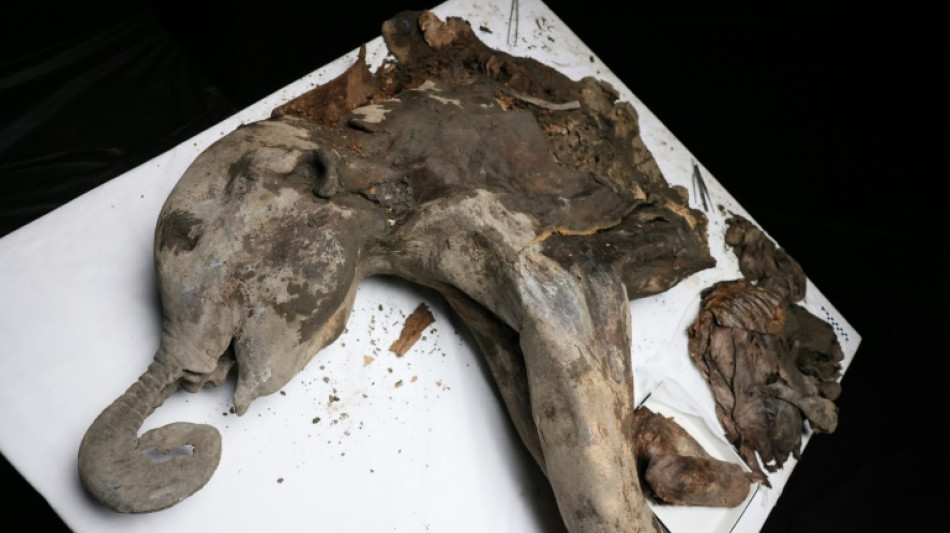
Yana, a 130,000-year-old baby mammoth, goes under the scalpel
Making incisions and carefully taking samples, the scientists at a laboratory in Russia's far east looked like pathologists carrying out a post-mortem.
But the body they were dissecting is a baby mammoth who died around 130,000 years ago.
Discovered last year, the calf -- nicknamed Yana, for the river basin where she was found -- is in a remarkable state of preservation, giving scientists a glimpse into the past and, potentially, the future as climate change thaws the permafrost in which she was found.
Yana's skin has kept its greyish-brown colour and clumps of reddish hairs. Her wrinkled trunk is curved and points to her mouth. The orbits of her eyes are perfectly recognisable and her sturdy legs resemble those of a modern-day elephant.
This necropsy -- an autopsy on an animal -- "is an opportunity to look into the past of our planet", said Artemy Goncharov, head of the Laboratory of Functional Genomics and Proteomics of Microorganisms at the Institute of Experimental Medicine in Saint Petersburg.
Scientists hope to find unique ancient bacteria and carry out genetic analysis of the plants and spores Yana ate to learn more about the place and time she lived.
The calf largely avoided the ravages of time because she lay for thousands of years encased in permafrost in the Sakha region in Siberia.
Measuring 1.2 metres (nearly four feet) at the shoulder and two metres long, and weighing 180 kilogrammes (nearly 400 pounds), Yana could be the best-preserved mammoth specimen ever found, retaining internal organs and soft tissues, the Russian scientists said.
- Stomach, intestines -
Dissecting her body is a treasure trove for the half-dozen scientists that were carrying out the necropsy in late March at the Mammoth Museum at North-Eastern Federal University in the regional capital, Yakutsk.
Wearing white sterile bodysuits, goggles and facemasks, the zoologists and biologists spent several hours working on the front quarters of the mammoth, a species that died out almost 4,000 years ago.
"We can see that many organs and tissues are very well preserved," Goncharov said.
"The digestive tract is partly preserved, the stomach is preserved. There are still fragments of the intestines, in particular the colon," enabling scientists to take samples, he said.
They are "searching for ancient microorganisms" preserved inside the mammoth, so they can study their "evolutionary relationship with modern microorganisms," he said.
While one scientist cut Yana's skin with scissors, another made an incision in the inner wall with a scalpel. They then placed tissue samples in test tubes and bags for analysis.
Another table held the mammoth's hindquarters, which remained embedded in a cliff when the front quarters fell below.
The scent emanating from the mammoth was reminiscent of a mixture of fermented earth and flesh, macerated in the Siberian subsoil.
"We are trying to reach the genitals," said Artyom Nedoluzhko, director of the Paleogenomics Laboratory of the European University at Saint Petersburg.
"Using special tools, we want to go into her vagina in order to gather material to understand what microbiota lived in her when she was alive."
- 'Milk tusks' -
Yana was first estimated to have died around 50,000 years ago, but is now dated at "more than 130,000 years" following analysis of the permafrost layer where she lay, said Maxim Cheprasov, director of the Mammoth Museum.
As for her age at death, "it's already clear that she is over a year old because her milk tusks have already appeared," he added.
Both elephants and mammoths have early milk tusks that later fall out.
Scientists are yet to determine why Yana died so young.
At the time when this herbivore mammal was chewing grass, "here on the territory of Yakutia there were not yet any humans", Cheprasov said, since they appeared in modern-day Siberia between 28,000 and 32,000 years ago.
The secret to Yana's exceptional preservation lies in the permafrost: the soil in this region of Siberia that is frozen year-round and acts like a gigantic freezer, preserving the carcasses of prehistoric animals.
The discovery of Yana's exposed body came about because of thawing permafrost, which scientists believe is due to global warming.
The study of the microbiology of such ancient remains also explores the "biological risks" of global warming, Goncharov said.
Some scientists are researching whether the melting permafrost could release potentially harmful pathogens, he explained.
"There are some hypotheses or conjectures that in the permafrost there could be preserved pathogenic microorganisms, which when it thaws can get into the water, plants and the bodies of animals -- and humans," he said.
O.Hansen--CPN

