-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount

-
 Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
-
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal

-
 Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
-
ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future

-
 EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
-
Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom

-
 Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
-
CNN's future unclear as Trump applies pressure

-
 German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases
German MPs approve 50 bn euros in military purchases
-
EU's Mercosur trade deal hits French, Italian roadblock

-
 Warner Bros rejects Paramount bid, sticks with Netflix
Warner Bros rejects Paramount bid, sticks with Netflix
-
Crude prices surge after Trump orders Venezuela oil blockade

-
 Warner Bros. Discovery rejects Paramount bid
Warner Bros. Discovery rejects Paramount bid
-
Doctors in England go on strike for 14th time

-
 Ghana's Highlife finds its rhythm on UNESCO world stage
Ghana's Highlife finds its rhythm on UNESCO world stage
-
Stocks gain as traders bet on interest rate moves

-
 France probes 'foreign interference' after malware found on ferry
France probes 'foreign interference' after malware found on ferry
-
Europe's Ariane 6 rocket puts EU navigation satellites in orbit

-
 Bleak end to the year as German business morale drops
Bleak end to the year as German business morale drops
-
Hundreds queue at Louvre museum as strike vote delays opening


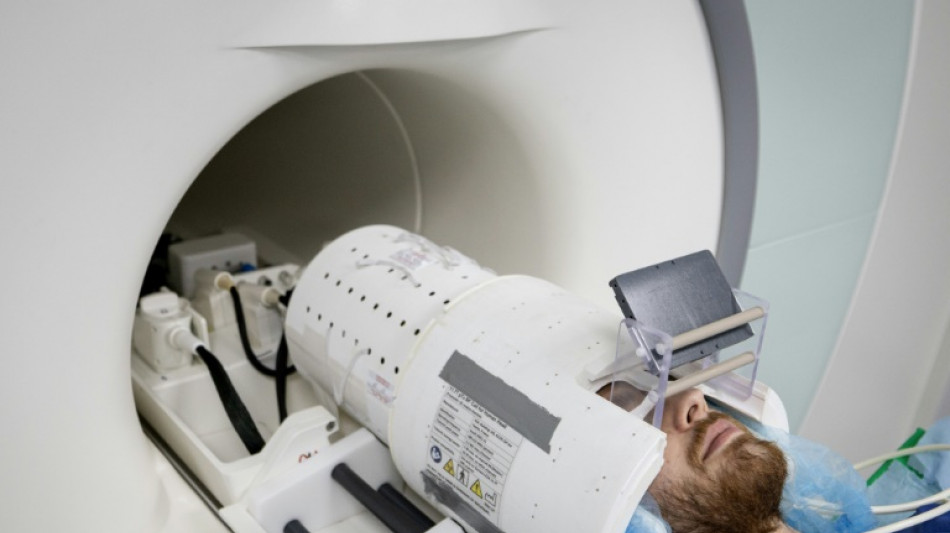
World's most powerful MRI scans first images of human brain
The world's most powerful MRI scanner has delivered its first images of human brains, reaching a new level of precision that is hoped will shed more light on our mysterious minds -- and the illnesses that haunt them.
Researchers at France's Atomic Energy Commission (CEA) first used the machine to scan a pumpkin back in 2021. But health authorities recently gave them the green light to scan humans.
Over the past few months, around 20 healthy volunteers have become the first to enter the maw of the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine, which is located in the Plateau de Saclay area south of Paris, home to many technology companies and universities.
"We have seen a level of precision never reached before at CEA," said Alexandre Vignaud, a physicist working on the project.
The magnetic field created by the scanner is a whopping 11.7 teslas, a unit of measurement named after inventor Nikola Tesla.
This power allows the machine to scan images with 10 times more precision than the MRIs commonly used in hospitals, whose power does not normally exceed three teslas.
On a computer screen, Vignaud compared images taken by this mighty scanner, dubbed Iseult, with those from a normal MRI.
"With this machine, we can see the tiny vessels which feed the cerebral cortex, or details of the cerebellum which were almost invisible until now," he said.
France's research minister Sylvie Retailleau, herself a physicist, said "the precision is hardly believable!"
"This world-first will allow better detection and treatment for pathologies of the brain," she said in a statement to AFP.
- Lighting up the brain's regions -
Inside a cylinder that is fives metres (16 feet) long and tall, the machine houses a 132-tonne magnet powered by a coil carrying a current of 1,500 amps.
There is a 90-centimetre (three-foot) opening for humans to slide into.
The design is the result of two decades of research by a partnership between French and German engineers.
The United States and South Korea are working on similarly powerful MRI machines, but have not yet started scanning images of humans.
One of the main goals of such a powerful scanner is to refine our understanding of the anatomy of the brain and which areas are activated when it carries out particular tasks.
Scientists have already used MRIs to show that when the brain recognises particular things -- such as faces, places or words -- distinct regions of the cerebral cortex kick into gear.
Harnessing the power of 11.7 teslas will help Iseult to "better understand the relationship between the brain's structure and cognitive functions, for example when we read a book or carry out a mental calculation," said Nicolas Boulant, the project's scientific director.
- On the trail of Alzheimer's -
The researchers hope that the scanner's power could also shed light on the elusive mechanisms behind neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's or Alzheimer's -- or psychological conditions like depression or schizophrenia.
"For example, we know that a particular area of the brain -- the hippocampus -- is implicated in Alzheimer's disease, so we hope to be able to find out how the cells work in this part of the cerebral cortex," said CEA researcher Anne-Isabelle Etienvre.
The scientists also hope to map out how certain drugs used to treat bipolar disorder, such as lithium, distribute through the brain.
The strong magnetic field created by the MRI will give a clearer image of which parts of the brain are targeted by lithium. This could help identify which patients will respond better or worse to the drug.
"If we can better understand these very harmful diseases, we should be able to diagnose them earlier -- and therefore treat them better," Etienvre said.
For the foreseeable future, regular patients will not be able to use Iseult's mighty power to see inside their own brains.
Boulant said the machine "is not intended to become a clinical diagnostic tool, but we hope the knowledge learned can then be used in hospitals".
In the coming months, a new crop of healthy patients will be recruited to get their brains scanned.
The machine will not be used on patients with conditions for several years.
Y.Ibrahim--CPN

