
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
'Family and intimacy under pressure' at Berlin film festival

-
 Asian markets extend gains as Tokyo enjoys another record day
Asian markets extend gains as Tokyo enjoys another record day
-
Unions rip American Airlines CEO on performance

-
 Jury told that Meta, Google 'engineered addiction' at landmark US trial
Jury told that Meta, Google 'engineered addiction' at landmark US trial
-
Three missing employees of Canadian miner found dead in Mexico

-
 Meta, Google face jury in landmark US addiction trial
Meta, Google face jury in landmark US addiction trial
-
Epstein accomplice Maxwell seeks Trump clemency before testimony

-
 Some striking NY nurses reach deal with employers
Some striking NY nurses reach deal with employers
-
Emergency measures kick in as Cuban fuel supplies dwindle under US pressure

-
 EU chief backs Made-in-Europe push for 'strategic' sectors
EU chief backs Made-in-Europe push for 'strategic' sectors
-
AI chatbots give bad health advice, research finds
-
 Iran steps up arrests while remaining positive on US talks
Iran steps up arrests while remaining positive on US talks
-
Bank of France governor Francois Villeroy de Galhau to step down in June

-
 EU warns Meta it must open up WhatsApp to rival AI chatbots
EU warns Meta it must open up WhatsApp to rival AI chatbots
-
Japan restarts world's biggest nuclear plant again

-
 Japan's Takaichi may struggle to soothe voters and markets
Japan's Takaichi may struggle to soothe voters and markets
-
'Want to go home': Indonesian crew abandoned off Africa demand wages

-
 Arguments to begin in key US social media addiction trial
Arguments to begin in key US social media addiction trial
-
Trump says China's Xi to visit US 'toward the end of the year'

-
 'Send Help' repeats as N.America box office champ
'Send Help' repeats as N.America box office champ
-
US astronaut to take her 3-year-old's cuddly rabbit into space

-
 UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy
UK foreign office to review pay-off to Epstein-linked US envoy
-
Storm-battered Portugal votes in presidential election run-off

-
 French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping
French police arrest five over crypto-linked magistrate kidnapping
-
De Beers sale drags in diamond doldrums

-
 What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
What's at stake for Indian agriculture in Trump's trade deal?
-
Pakistan's capital picks concrete over trees, angering residents

-
 Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
Neglected killer: kala-azar disease surges in Kenya
-
Chile's climate summit chief to lead plastic pollution treaty talks

-
 Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain
-
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection

-
 Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users
-
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo

-
 Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe
-
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles

-
 Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer

-
 Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns
-
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost

-
 Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift
-
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe

-
 In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school
-
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters

-
 As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle
-
Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts

-
 Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote
Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote
-
Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant

-
 UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall
UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall
-
Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer


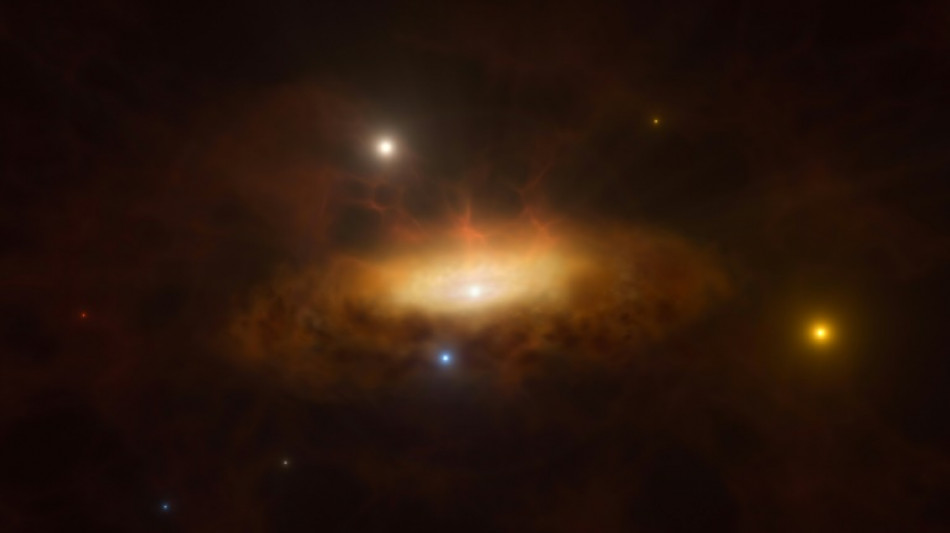
Massive black hole 'waking up' in Virgo constellation
A massive black hole at the heart of a galaxy in the Virgo constellation is waking up, shooting out intense X-ray flares at regular intervals that have puzzled scientists, a study said Friday.
Astronomers previously had little reason to pay any attention to galaxy SDSS1335+0728, which is 300 million light years from Earth.
But in 2019, the galaxy suddenly started shining with a brightness that turned some telescopes its way.
Then in February last year, Chilean astronomers started noticing regular bursts of X-rays coming from the galaxy.
This was a sign that the galaxy's sleeping black hole was waking from its slumber, according to the study published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Most galaxies, including our home Milky Way, have a supermassive black hole squatting at their heart, like a spider in a web.
These invisible monsters gobble up everything that comes their way -- not even light can escape their almighty suck.
If an unlucky star swings too close, it gets torn apart.
The star's shattered material becomes a stream that spins rapidly around the black hole, forming what is called an accretion disc that is gradually swallowed.
But black holes can also go through long periods of inactivity when they do not attract matter.
And after a fairly uneventful period, the bright, compact region at the heart of galaxy SDSS1335+0728 has been classified as an "active galactic nucleus" -- and given the nickname "Ansky".
"This rare event provides an opportunity for astronomers to observe a black hole's behaviour in real time" using several X-ray telescopes, astronomer Lorena Hernandez-Garcia of Chile's Valparaiso University said in a statement.
- 'Pushes models to their limits' -
Ansky's short-lived X-ray flares are called quasiperiodic eruptions, or QPEs.
"This is the first time we have observed such an event in a black hole that seems to be waking up," Hernandez-Garcia said.
"We don't yet understand what causes them."
The current theory is that QPEs are linked to the accretion discs that form after black holes swallow stars.
But there is no sign that Ansky has recently feasted on a star.
And its flares are quite unusual.
"The bursts of X-rays from Ansky are 10 times longer and 10 times more luminous than what we see from a typical QPE," said Joheen Chakraborty, a PhD student at MIT and member of the research team.
"Each of these eruptions is releasing a hundred times more energy than we have seen elsewhere."
The intervals of 4.5 days between these blasts are also the longest ever observed, he added.
"This pushes our models to their limits and challenges our existing ideas about how these X-ray flashes are being generated," he said in the statement.
Astronomers have had to come up with some theories for what could be causing these strange bursts.
One was that the accretion disc was formed by gas getting sucked into the black hole, which only shoots out X-ray flares when a small celestial object such as a star crosses its path.
"Simply imagine a black hole and disc around it," Norbert Schartel, chief scientist of the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton telescope which has observed Ansky, told AFP.
Now imagine the star crossing the disc twice every time it orbits -- shooting out flares -- but at a particular angle which means "there is no real strong force to drag it in," he said.
X-ray astronomer Erwan Quintin told AFP that "for QPEs, we're still at the point where we have more models than data".
"We need more observations to understand what's happening."
M.P.Jacobs--CPN


