-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Ghana moves to rewrite mining laws for bigger share of gold revenues

-
 Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
Russia's sanctioned oil firm Lukoil to sell foreign assets to Carlyle
-
Gold soars towards $5,600 as Trump rattles sabre over Iran

-
 Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
Deutsche Bank logs record profits, as new probe casts shadow
-
Vietnam and EU upgrade ties as EU chief visits Hanoi

-
 Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
Hongkongers snap up silver as gold becomes 'too expensive'
-
Gold soars past $5,500 as Trump sabre rattles over Iran

-
 Samsung logs best-ever profit on AI chip demand
Samsung logs best-ever profit on AI chip demand
-
China's ambassador warns Australia on buyback of key port

-
 As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
As US tensions churn, new generation of protest singers meet the moment
-
Venezuelans eye economic revival with hoped-for oil resurgence

-
 Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
Samsung Electronics posts record profit on AI demand
-
French Senate adopts bill to return colonial-era art

-
 Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
Tesla profits tumble on lower EV sales, AI spending surge
-
Meta shares jump on strong earnings report

-
 Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary
Anti-immigration protesters force climbdown in Sundance documentary
-
Springsteen releases fiery ode to Minneapolis shooting victims

-
 SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report
SpaceX eyes IPO timed to planet alignment and Musk birthday: report
-
Neil Young gifts music to Greenland residents for stress relief

-
 Fear in Sicilian town as vast landslide risks widening
Fear in Sicilian town as vast landslide risks widening
-
King Charles III warns world 'going backwards' in climate fight

-
 Court orders Dutch to protect Caribbean island from climate change
Court orders Dutch to protect Caribbean island from climate change
-
Rules-based trade with US is 'over': Canada central bank head

-
 Holocaust survivor urges German MPs to tackle resurgent antisemitism
Holocaust survivor urges German MPs to tackle resurgent antisemitism
-
'Extraordinary' trove of ancient species found in China quarry

-
 Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
Google unveils AI tool probing mysteries of human genome
-
UK proposes to let websites refuse Google AI search

-
 Trump says 'time running out' as Iran threatens tough response
Trump says 'time running out' as Iran threatens tough response
-
Germany cuts growth forecast as recovery slower than hoped

-
 Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
Amazon to cut 16,000 jobs worldwide
-
Greenland dispute is 'wake-up call' for Europe: Macron

-
 Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
Dollar halts descent, gold keeps climbing before Fed update
-
Sweden plans to ban mobile phones in schools

-
 Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
Deutsche Bank offices searched in money laundering probe
-
Susan Sarandon to be honoured at Spain's top film awards

-
 Trump says 'time running out' as Iran rejects talks amid 'threats'
Trump says 'time running out' as Iran rejects talks amid 'threats'
-
Spain eyes full service on train tragedy line in 10 days

-
 Greenland dispute 'strategic wake-up call for all of Europe,' says Macron
Greenland dispute 'strategic wake-up call for all of Europe,' says Macron
-
SKorean chip giant SK hynix posts record operating profit for 2025

-
 Greenland's elite dogsled unit patrols desolate, icy Arctic
Greenland's elite dogsled unit patrols desolate, icy Arctic
-
Uganda's Quidditch players with global dreams

-
 'Hard to survive': Kyiv's elderly shiver after Russian attacks on power and heat
'Hard to survive': Kyiv's elderly shiver after Russian attacks on power and heat
-
Polish migrants return home to a changed country

-
 Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, eyes bright AI future
Dutch tech giant ASML posts bumper profits, eyes bright AI future
-
Minnesota congresswoman unbowed after attacked with liquid

-
 Backlash as Australia kills dingoes after backpacker death
Backlash as Australia kills dingoes after backpacker death
-
Omar attacked in Minneapolis after Trump vows to 'de-escalate'

-
 Dollar struggles to recover from losses after Trump comments
Dollar struggles to recover from losses after Trump comments
-
Greenland blues to Delhi red carpet: EU finds solace in India


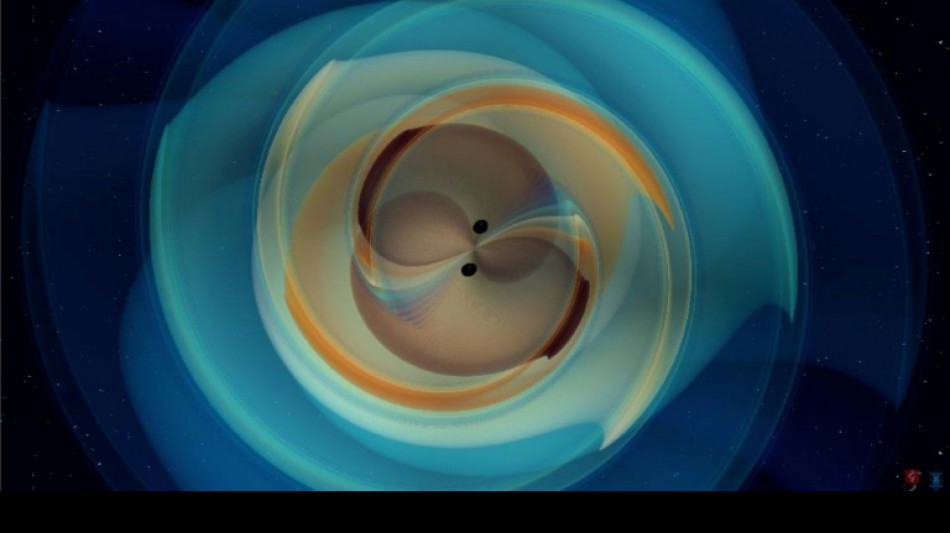
Gravitational waves from black hole smash confirm Hawking theory
Ripples in spacetime sent hurtling through the universe when two black holes smash into each other -- a phenomenon predicted by Albert Einstein -- have confirmed a theory proposed by fellow physicist Stephen Hawking over 50 years ago, scientists announced Wednesday.
These ripples, which are called gravitational waves, were detected for the first time in 2015 by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) in the United States.
In his 1916 theory of general relativity, Einstein predicted that the cataclysmic merger of two black holes would produce gravitational waves that would ripple across the universe and eventually arrive at Earth.
On January 14 this year, LIGO detected another of these signals from the distant universe.
That is no longer such a surprise.
Scientists in the LVK collaboration -- a vast network of scientists whose facilities includes gravitational wave detectors in Italy and Japan -- now record a new black hole merger roughly once every three days.
However January was "the loudest gravitational wave event we have detected to date," LIGO member Geraint Pratten of the University of Birmingham, England, said in a statement.
- From a whisper to a shout -
"It was like a whisper becoming a shout," added the co-author of a new study in the Physical Review Letters.
The latest event bore striking similarities to the first one detected a decade ago.
Both involved collisions of black holes with masses of between 30-40 times that of our Sun. And both smash-ups occurred around 1.3 billion light years away.
But thanks to technological improvements over the years, scientists are now able to greatly reduce the background noise, giving them far clearer data.
This allowed the researchers to confirm a theory by another great physicist.
In 1971, Stephen Hawking predicted that a black hole's event horizon -- the area from which nothing including light can escape -- cannot shrink.
This means that when two black holes merge, the new monster they create must have the same or larger surface area than the pair started out with.
Scientists analysing January's merger, called GW250114, were able to show that Hawking was right.
- Ringing like a struck bell -
The black holes collectively started out at 240,000 square kilometres wide, which is roughly the size of the United Kingdom.
But after the collision, the resulting mega-black hole took up 400,000 square kilometres -- about the size of Sweden.
The California Institute of Technology said that working out the final merged surface area was "the trickiest part of this type of analysis".
"The surface areas of pre-merger black holes can be more readily gleaned as the pair spiral together, roiling space-time and producing gravitational waves," it said in a statement.
But the signal gets muddier once the black holes start combining into a single new monster.
This period is called the "ringdown phase", because the merged black hole rings like a struck bell -- a phenomenon that Einstein also predicted.
The scientists were able to measure different frequencies emanating from this rung bell, allowing them to determine the size of the new post-merger black hole.
- Kerr theory vindicated -
This also enabled them to confirm the event aligned with another theory, made by New Zealand mathematician Roy Kerr in 1963.
Kerr predicted that "two black holes with the same mass and spin are mathematically identically," a feature unique to black holes, Maximiliano Isi of Columbia University said in a statement.
Gregorio Carullo of the University of Birmingham said that "given the clarity of the signal produced by GW250114, for the first time we could pick out two 'tones' from the black hole voices and confirm that they behave according to Kerr's prediction."
Scientists are working to find out more about black hole mergers, with several new gravitational wave detectors planned for the coming years -- including one in India.
A.Mykhailo--CPN

