
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Spain, Portugal face fresh storms, torrential rain

-
 Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
Opinions of Zuckerberg hang over social media addiction trial jury selection
-
Crypto firm accidentally sends $40 bn in bitcoin to users

-
 Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
Dow surges above 50,000 for first time as US stocks regain mojo
-
Danone expands recall of infant formula batches in Europe

-
 EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
EU nations back chemical recycling for plastic bottles
-
Why bitcoin is losing its luster after stratospheric rise
-
 Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
Stocks rebound though tech stocks still suffer
-
Digital euro delay could leave Europe vulnerable, ECB warns

-
 German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
German exports to US plunge as tariffs exact heavy cost
-
Stellantis takes massive hit for 'overestimation' of EV shift

-
 'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
'Mona's Eyes': how an obscure French art historian swept the globe
-
In Dakar fishing village, surfing entices girls back to school

-
 Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
Russian pensioners turn to soup kitchen as war economy stutters
-
As Estonia schools phase out Russian, many families struggle

-
 Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
Toyota names new CEO, hikes profit forecasts
-
Bangladesh Islamist leader seeks power in post-uprising vote

-
 Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
Japan to restart world's biggest nuclear plant
-
UK royal finances in spotlight after Andrew's downfall

-
 Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
Undercover probe finds Australian pubs short-pouring beer
-
New Zealand deputy PM defends claims colonisation good for Maori

-
 Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
Amazon shares plunge as AI costs climb
-
Deadly storm sparks floods in Spain, raises calls to postpone Portugal vote

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate, affirms auto sector's future is electric
-
Lower pollution during Covid boosted methane: study

-
 Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
Carney scraps Canada EV sales mandate
-
Record January window for transfers despite drop in spending

-
 Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
Mining giant Rio Tinto abandons Glencore merger bid
-
Davos forum opens probe into CEO Brende's Epstein links

-
 ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
ECB warns of stronger euro impact, holds rates
-
Greece aims to cut queues at ancient sites with new portal

-
 ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
ECB holds interest rates as strong euro causes jitters
-
What does Iran want from talks with the US?

-
 Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
Wind turbine maker Vestas sees record revenue in 2025
-
Bitcoin under $70,000 for first time since Trump's election

-
 Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
Germany claws back 59 mn euros from Amazon over price controls
-
Germany claws back 70 mn euros from Amazon over price controls

-
 Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
Stock markets drop amid tech concerns before rate calls
-
BBVA posts record profit after failed Sabadell takeover

-
 UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
UN human rights agency in 'survival mode': chief
-
Greenpeace slams fossel fuel sponsors for Winter Olympics

-
 Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
Russia says thwarted smuggling of giant meteorite to UK
-
Heathrow still Europe's busiest airport, but Istanbul gaining fast

-
 Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
Shell profits climb despite falling oil prices
-
German factory orders rise at fastest rate in 2 years in December

-
 Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
Trump fuels EU push to cut cord with US tech
-
Top US news anchor pleads with kidnappers for mom's life

-
 The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
The coming end of ISS, symbol of an era of global cooperation
-
New crew set to launch for ISS after medical evacuation


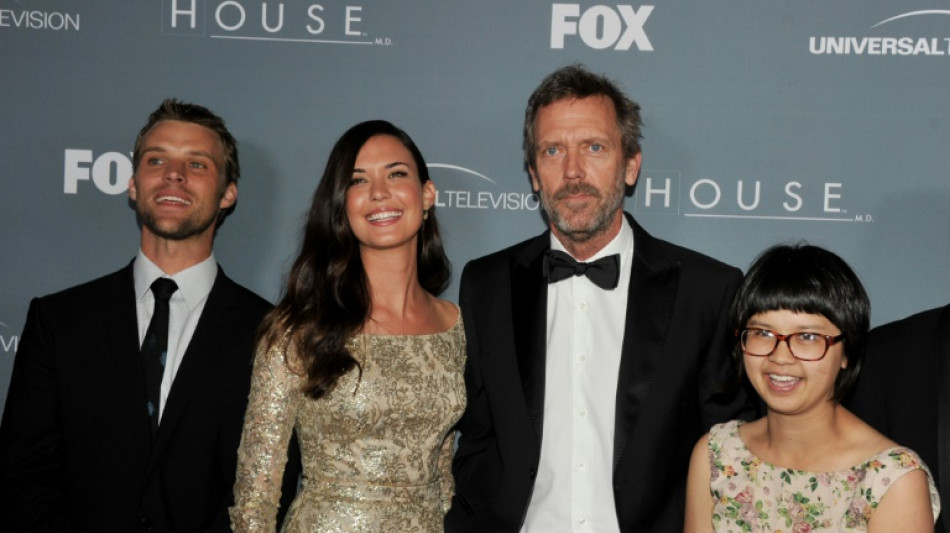
Experts point out how TV's Dr House often got it wrong
He's the maverick medic who loved to confound the medical establishment with his brilliant, unorthodox diagnoses.
But Dr Gregory House, the misanthropic genius who was the star of the long-running "House" television series, got an awful lot wrong himself, Croatian doctors claim.
From a neurologist at work on the wrong end of a patient by performing a colonoscopy, or an MRI scan done by a physician who is clearly not a radiologist, Croatian researchers have pulled the American series up on its medical accuracy in a paper published this month.
Denis Cerimagic, a professor at Dubrovnik University, and two fellow neurologists -- all big fans of the series -- listed 77 errors after analysing all 177 episodes of the show, which ran from 2004 to 2012.
"We focused on the diagnoses of main cases, reality of clinical practice presentation and detection of medical errors," Cerimagic told AFP.
He and his peers -- Goran Ivkic and Ervina Bilic -- broke the mistakes down into five categories including misuses of medical terminology, misinformation and simple weirdness -- something which the show's anti-hero, played by British star Hugh Laurie, possessed in abundance.
- That limp -
They included the use of mercury thermometers -- which had long given way to digital ones -- the term heart attack and cardiac arrest being used interchangeably when they are not the same, and that vitamin B12 deficiency can be corrected with just one injection.
Nor is there a universal chemotherapy for all types of malignant tumours, as one episode suggested.
But arguably the biggest error of all is that Laurie -- whose character's genius for deduction comes from the misdiagnosis that left him with a limp and chronic pain -- uses his cane on the wrong side.
The stick should be carried on his unaffected side, Cerimagic said, though he understood why the actor had done it because "it's more effective to see the pronounced limp on the screen".
Their research also found medical procedures being done by specialists who had no business being there, like an infectologist performing an autopsy.
At times the series also stretched reality beyond breaking point, with the findings of complex laboratory tests done in just a few hours. And doctors rarely turn detective and take it upon themselves to enter patients' homes to look for environmental causes of illnesses.
Not to mention Dr House's unethical behaviour -- "Brain tumour, she's gonna die" the paper quoted him as saying -- and the character's opiates addiction.
The researchers say they may have missed other mistakes.
"We are neurologists while other medical specialists would certainly establish additional errors," Cerimagic added.
- Medical errors -
Whatever their criticisms, the researchers say that modern medical series are far better produced than in the past, thanks to medical advisors.
It is not like some 20 years ago when you had doctors looking at X-rays upside down, the neurologist said.
"Now only medical professionals can notice errors," Cerimagic said.
Despite its flaws, they thought the series could even be used to help train medical students.
"The focus could be on recognising medical errors in the context of individual episodes, adopting the teamwork concept and a multidisciplinary approach in diagnosis and treatment," Cerimagic said.
He said he and his colleagues were taken aback by the response to their paper "House M.D.: Between reality and fiction" -- which is not the first academic study to cast doubt on the good doctor and his methods.
"The idea was to make a scientific paper interesting not only to doctors but also to people without specific medical knowledge."
J.Bondarev--CPN


