
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Fuming Denmark summons US ambassador over Greenland envoy

-
 Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations
Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations
-
Sri Lanka cyclone caused $4.1 bn damage: World Bank

-
 Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
-
Tech stocks lead Wall Street higher, gold hits fresh record

-
 Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
-
EU slams China dairy duties as 'unjustified'

-
 Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese

-
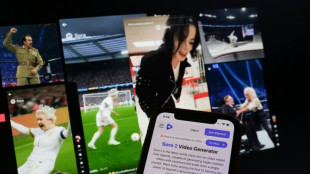 AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
-
Wheelchair user flies into space, a first

-
 French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
-
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack

-
 Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
-
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide

-
 IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount


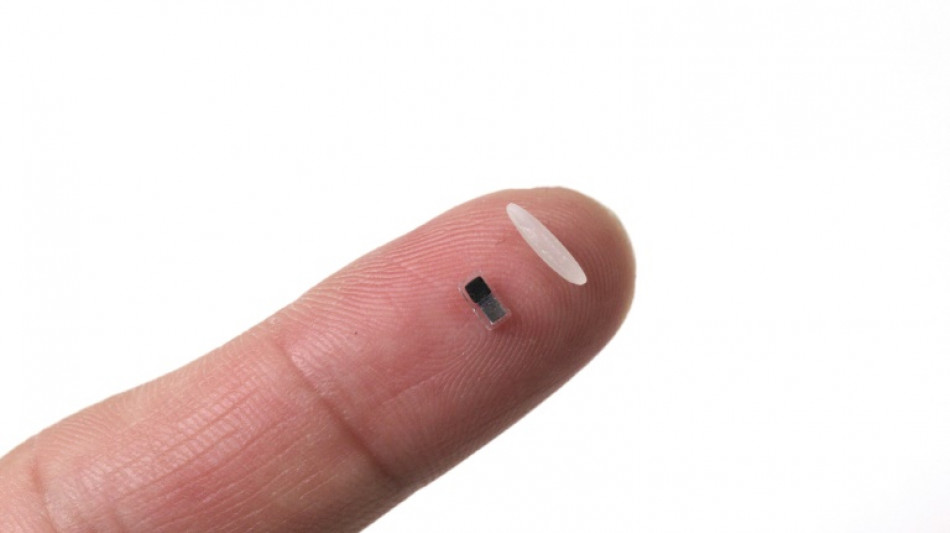
World's tiniest pacemaker is smaller than grain of rice
Scientists said Wednesday they have developed the world's tiniest pacemaker, a temporary heartbeat regulator smaller than a grain of rice that can be injected and controlled by light before dissolving.
While still years away from being tested in humans, the wireless pacemaker was hailed as a "transformative breakthrough" that could spur advances in other areas of medicine.
Millions of people across the world have permanent pacemakers, which stimulate hearts with electrical pulses to ensure they beat normally.
The US-led team of researchers behind the new device said they were motivated to help the one percent of children born with congenital heart defects who need a temporary pacemaker in the week after surgery.
The pacemaker could also help adults restore a normal heartbeat as they recover from heart surgery.
Currently, temporary pacemakers require surgery to sew electrodes onto heart muscles, with wires connecting to a powered device on the patient's chest.
When the pacemaker is no longer needed, doctors or nurses pull out the wires, which can sometimes cause damage.
Neil Armstrong, the first person to walk on the Moon, died from internal bleeding after his temporary pacemaker was removed in 2012.
But the newly developed pacemaker is wireless. And at just one millimetre thick and 3.5 millimetres long, it can fit into the tip of a syringe.
It has also been designed to dissolve into the body when no longer needed, sparing patients invasive surgery.
- 'Significant leap forward' -
The pacemaker is paired to a soft patch worn on the patient's chest, according to a study describing the device in the journal Nature.
When the patch detects irregular heartbeats, it automatically flashes light that tells the pacemaker what heartbeat it should stimulate.
The pacemaker is powered by what is called a galvanic cell, which uses the body's fluids to convert chemical energy into electrical pulses that stimulate the heart.
So far, the pacemaker has worked effectively in tests on mice, rats, pigs, dogs and human heart tissue in the lab, according to the study.
Senior study author John Rogers of Northwestern University in the United States told AFP he estimated the pacemaker could be tested in humans in two to three years.
His lab has launched a start-up to pursue this goal, he added.
In the future, the underlying technology could also "create unique and powerful strategies to address societal challenges in human health," Rogers said.
Bozhi Tian, whose lab at the University of Chicago has also developed light-activated pacemakers but was not involved in the latest research, called it a "significant leap forward".
"This new pacemaker is a transformative breakthrough in medical technology," he told AFP.
"It's a paradigm shift in temporary pacing and bioelectronic medicine, opening up possibilities far beyond cardiology -- including nerve regeneration, wound healing and integrated smart implants."
Heart disease is the world's leading cause of death, according to the World Health Organization.
St.Ch.Baker--CPN


