
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Fuming Denmark summons US ambassador over Greenland envoy

-
 Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations
Outcry follows CBS pulling program on prison key to Trump deportations
-
Sri Lanka cyclone caused $4.1 bn damage: World Bank

-
 Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
-
Tech stocks lead Wall Street higher, gold hits fresh record

-
 Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
-
EU slams China dairy duties as 'unjustified'

-
 Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese

-
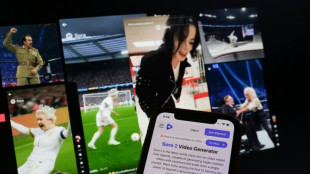 AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
-
Wheelchair user flies into space, a first

-
 French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
-
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack

-
 Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
-
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide

-
 IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount


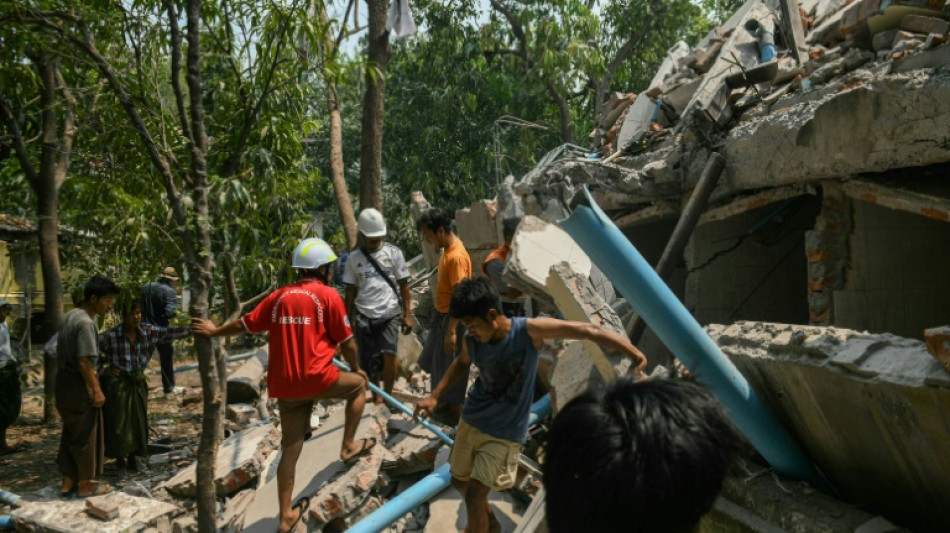
Scientists explain why Myanmar quake was so deadly
Experts say that the devastating earthquake in Myanmar on Friday was likely the strongest to hit the country in decades, with disaster modelling suggesting thousands could be dead.
Automatic assessments from the United States Geological Survey (USGS) said the shallow 7.7-magnitude quake northwest of the central Myanmar city of Sagaing triggered a red alert for shaking-related fatalities and economic losses.
"High casualties and extensive damage are probable and the disaster is likely widespread," it said, locating the epicentre near the central Myanmar city of Mandalay, home to more than a million people.
Myanmar's ruling junta said on Saturday morning that the number killed had passed 1,000, with more than 2,000 injured.
However, the USGS analysis said there was a 35 percent chance that possible fatalities could be in the range of 10,000-100,000 people.
The USGS offered a similar likelihood that the financial damage could total tens of thousands of millions of dollars, warning that it might exceed the GDP of Myanmar.
Weak infrastructure will complicate relief efforts in the isolated, military-ruled state, where rescue services and the healthcare system have already been ravaged by four years of civil war sparked by a military coup in 2021.
- Dangerous fault -
Bill McGuire, emeritus professor of geophysical and climate hazards at University College London (UCL), said it was "probably the biggest earthquake on the Myanmar mainland in three-quarters of a century".
A 6.7-magnitude aftershock struck minutes after the first and McGuire warned that "more can be expected".
Rebecca Bell, a tectonics expert at Imperial College London (ICL), suggested it was a side-to-side "strike-slip" of the Sagaing Fault.
This is where the Indian tectonic plate, to the west, meets the Sunda plate that forms much of Southeast Asia -- a fault similar in scale and movement to the San Andreas Fault in California.
"The Sagaing fault is very long, 1,200 kilometres (745 miles), and very straight," Bell said. "The straight nature means earthquakes can rupture over large areas -- and the larger the area of the fault that slips, the larger the earthquake."
Earthquakes in such cases can be "particularly destructive", Bell added, explaining that since the quake takes place at a shallow depth, its seismic energy has dissipated little by the time it reaches populated areas above.
That causes "a lot of shaking at the surface", Bell said.
- Building boom -
Myanmar has been hit by powerful quakes in the past.
There have been more than 14 earthquakes with a magnitude of 6 or above in the past century, including a magnitude 6.8 earthquake near Mandalay in 1956, said Brian Baptie, a seismologist with the British Geological Survey.
Ian Watkinson, from the department of earth sciences at Royal Holloway University of London, said what had changed in recent decades was the "boom in high-rise buildings constructed from reinforced concrete".
Myanmar has been riven by years of conflict and there is a low level of building design enforcement.
"Critically, during all previous magnitude 7 or larger earthquakes along the Sagaing Fault, Myanmar was relatively undeveloped, with mostly low-rise timber-framed buildings and brick-built religious monuments," Watkinson said.
"Today's earthquake is the first test of modern Myanmar's infrastructure against a large, shallow-focus earthquake close to its major cities."
Baptie said that at least 2.8 million people in Myanmar were in hard-hit areas where most lived in buildings "constructed from timber and unreinforced brick masonry" that are vulnerable to earthquake shaking.
"The usual mantra is that 'earthquakes don't kill people; collapsing infrastructure does'," said Ilan Kelman, an expert in disaster reduction at UCL.
"Governments are responsible for planning regulations and building codes. This disaster exposes what governments of Burma/Myanmar failed to do long before the earthquake, which would have saved lives during the shaking."
- Skyscraper checks -
Strong tremors also rocked neighbouring Thailand, where a 30-storey skyscraper under construction was reduced to a pile of dusty concrete, trapping workers in the debris.
Christian Malaga-Chuquitaype, from ICL's civil and environmental engineering department, said the nature of the ground in Bangkok contributed to the impact on the city, despite being some 1,000 kilometres (620 miles) from the epicentre in Myanmar.
"Even though Bangkok is far from active faults, its soft soil amplifies the shaking," he said. "This affects especially tall buildings during distant earthquakes."
Malaga-Chuquitaype said the construction techniques in Bangkok favouring "flat slabs" -- where floors are held only by columns without using strengthening beams, like a table supported only by legs -- were a "problematic design".
He said that initial video analysis of the collapsed tower block in Bangkok suggested this type of construction technique had been used.
Roberto Gentile, a catastrophe risk modelling expert from UCL, said the "dramatic collapse" of the Bangkok tower block meant that "other tall buildings in the city may require a thorough assessment".
Bangkok city authorities said they will deploy more than 100 engineers to inspect buildings for safety after receiving more than 2,000 reports of damage.
X.Wong--CPN


