
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Sri Lanka cyclone caused $4.1 bn damage: World Bank

-
 Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
Billionaire Ellison offers personal guarantee for son's bid for Warner Bros
-
Tech stocks lead Wall Street higher, gold hits fresh record

-
 Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
Telefonica to shed around 5,500 jobs in Spain
-
EU slams China dairy duties as 'unjustified'

-
 Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese

-
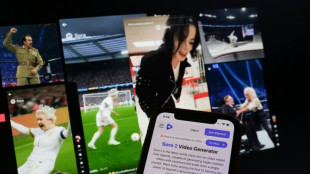 AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
-
Wheelchair user flies into space, a first

-
 French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
-
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack

-
 Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
-
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide

-
 IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount

-
 Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
-
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal


Tech firms fight to stem deepfake deluge
Tech firms are fighting the scourge of deepfakes, those deceptively realistic voices or videos used by scammers that are more available than ever thanks to artificial intelligence.
Ever-improving generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) tools have become weapons in the hands of bad actors intent on tricking people out of their money or even their identities.
Debby Bodkin tells of her 93-year-old mother receiving a telephone call, a cloned voice claiming, "It's me, mom... I've had an accident."
When asked where they were, the machine-made impersonator named a hospital.
Fortunately, it was a granddaughter who answered the phone, opting to hang up and call Bodkin at work where she was safe and well.
"It's not the first time scammers have called grandma," Bodkin told AFP. "It's daily."
Such deepfake phone scams typically go on to coax victims into paying for medical care or other made-up emergencies.
Used on social networks to hijack the notoriety of celebrities or other high-profile figures, sometimes for disinformation, deepfakes are also being exploited by criminal gangs.
Hong Kong police earlier this year revealed that a multinational firm employee was tricked into wiring HK$200 million (around US$26 million) to crooks who staged a videoconference with AI avatars of his colleagues.
A recent study by identification start-up iBoom found that a scant tenth of one percent of Americans and Britons were able to correctly tell when a picture or video was a deepfake.
A decade ago, there was a single AI tool for generating synthetic voices -- now there are hundreds of them, according to voice authentication specialist Vijay Balasubramaniyan, CEO of Pindrop Security.
GenAI has changed the game, he said.
"Before, it took 20 hours (of voice recording) to recreate your voice," the executive told AFP.
"Now, it's five seconds."
Firms such as Intel have stepped up with tools to detect GenAI-made audio or video in real-time.
Intel "FakeCatcher" detects color changes in facial blood vessels to distinguish genuine from bogus imagery.
Pindrop breaks down every second of audio and compares it with characteristics of a human voice.
"You have to keep up with the times," says Nicos Vekiarides, chief of Attestiv platform which specializes in authenticating digital creations.
"In the beginning, we saw people with six fingers on one hand, but progress has made it harder and harder to tell (deepfakes) with the naked eye."
- 'Global cybersecurity threat' -
Balasubramaniyan believes that software for spotting AI content will become standard at companies of all kinds.
While GenAI has blurred the boundary between human and machine, companies that re-establish that divide could soar in a market that will be worth billions of dollars, he said.
Vekiarides warned that the issue "is becoming a global cybersecurity threat."
"Any company can have its reputation tarnished by a deepfake or be targeted by these sophisticated attacks," Vekiarides said.
Balasubramaniyan added that the shift to telework provides more opportunity for bad actors to impersonate their way into companies.
Beyond the corporate world, many expect consumers to look for ways to fight off deepfake scams endangering their personal lives.
In January, China-based Honor unveiled a Magic7 smartphone with a built-in deepfake detector powered by AI.
British start-up Surf Security late last year launched a web browser that can flag synthetic voice or video, aiming it at businesses.
Siwei Lyu, a professor of computer science at the State University of New York at Buffalo, believes "deepfakes will become like spam," an internet nightmare that people eventually get under control.
"Those detection algorithms will be like spam filters in our email software," Lyu predicted.
"We're not there yet."
Ch.Lefebvre--CPN


