
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
EU slams China dairy duties as 'unjustified'

-
 Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Stocks diverge as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese

-
 AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
-
Wheelchair user flies into space, a first

-
 French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
-
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack

-
 Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
-
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide

-
 IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount

-
 Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
-
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal

-
 Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
-
ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future

-
 EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
-
Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom


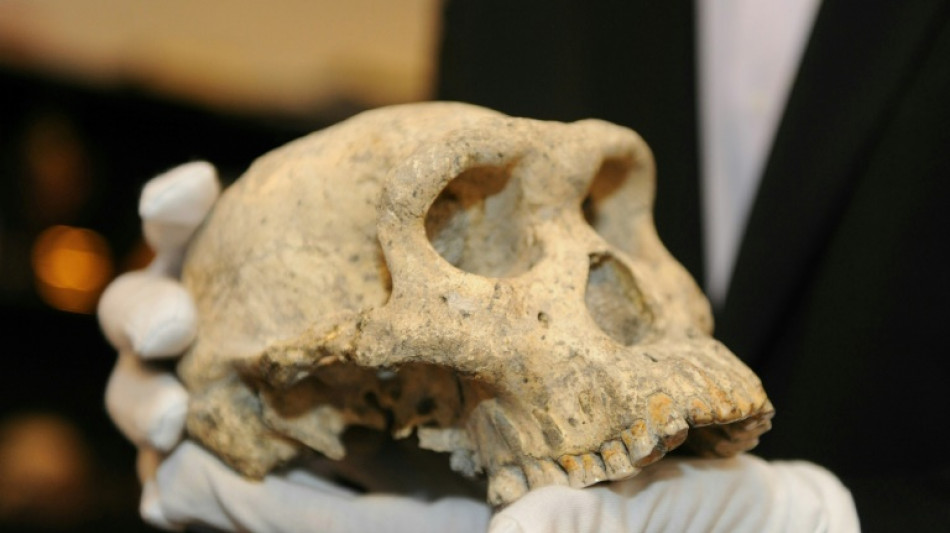
Meet 'Pink', the new face of human evolution in Europe
Western Europe has a new oldest face: the facial bones of an adult nicknamed "Pink" discovered in Spain are from a potential new member of the human family who lived more than 1.1 million years ago, scientists said Wednesday.
Until now, the oldest-known human species in Western Europe was the slender-faced Homo antecessor, dating back around 850,000 years.
But research published in the journal Nature "introduces a new actor in the history of human evolution in Europe", lead study author Rosa Huguet of Spain's University of Rovira i Virgili told a press conference.
The fossilised upper jawbone and partial cheekbone of Pink were discovered at the Atapuerca archaeological site in northern Spain in 2022.
Since then, a team of Spanish scientists have been working to find out more about Pink, whose nickname is a reference to prog rock band Pink Floyd.
The bones were excavated from a layer of silt and red mud 16 metres (52 feet) deep at a site known as Sima del Elefante -- or "elephant pit".
They were found less than 250 metres from where the fossils of Western Europe's previous oldest human, Homo antecessor, were discovered nearly two decades ago.
But the title of oldest human in all of Europe is still held by the Dmanisi people -- also called Homo georgicus -- who lived up to 1.8 million years ago in what is now Georgia.
They were the first members of the human family, or hominins, known to have made it to Europe from Africa, the cradle of humanity.
We modern Homo sapiens first showed up in Africa around 300,000 years ago -- and took our time getting to Europe.
- Face value -
The Spanish researchers used 3D imaging techniques to flesh out Pink's full face.
Homo antecessor had a "very modern" face which is "vertical and flat" similar to our own, said Maria Martinon-Torres, director of Spain's National Research Center on Human Evolution.
But Pink's face is more "projected forward and more robust," the study co-author added.
This means it bears some similarities to the face of Homo erectus -- but not enough that the scientists could confirm that Pink was a member of this important human ancestor.
So the scientists made up a new name for the possible species that Pink could belong to: Homo "affinis" erectus.
"This is the most honest proposal we can make with the evidence we have," Martinon-Torres said.
From just a few face bones, the researchers could not determine Pink's age or gender.
But by analysing small stone tools and animals bones found at the site, they were able to get an idea of the environment Pink lived in.
It was a humid forest landscape, roamed by horses, ancient cattle, monkeys and even some hippos.
The area was a wildlife corridor with plenty of water, making it an "ideal" place for our ancient relatives to settle, Huguet said.
- What happened to them? -
The new discovery supports the hypothesis that early humans settled Europe going from east to west at least 1.4 million years ago, according to the Spanish researchers.
If Pink is a representative of a previously unknown human species, it could have been a bridge between the Dmanisi hominins and Homo antecessors, they added.
But this raises another question: what became of these people?
Spanish paleoanthropologist Jose Maria Bermudez de Castro felt that Pink's people likely did not survive a severe human "bottleneck" nearly 900,000 years ago thought to have been caused by global cooling.
"I think that Homo affinis erectus probably disappeared," the study co-author said.
Future research will aim to shed light on these mysteries. The Spanish team has not yet reached the bottom of the elephant pit -- nor other sites around it.
H.Meyer--CPN


