
-
 Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
Kenya's economy faces climate change risks: World Bank
-
Swiss court to hear landmark climate case against cement giant

-
 Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
Asian markets rally with Wall St as rate hopes rise, AI fears ease
-
As US battles China on AI, some companies choose Chinese

-
 AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
AI resurrections of dead celebrities amuse and rankle
-
Third 'Avatar' film soars to top in N. American box office debut

-
 China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
China's rare earths El Dorado gives strategic edge
-
Wheelchair user flies into space, a first

-
 French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
French culture boss accused of mass drinks spiking to humiliate women
-
US Afghans in limbo after Washington soldier attack

-
 Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
Nasdaq rallies again while yen falls despite BOJ rate hike
-
US university killer's mystery motive sought after suicide

-
 IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
IMF approves $206 mn aid to Sri Lanka after Cyclone Ditwah
-
Rome to charge visitors for access to Trevi Fountain

-
 Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
Stocks advance with focus on central banks, tech
-
Norway crown princess likely to undergo lung transplant

-
 France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
France's budget hits snag in setback for embattled PM
-
Volatile Oracle shares a proxy for Wall Street's AI jitters

-
 Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
Japan hikes interest rates to 30-year-high
-
Brazil's top court strikes down law blocking Indigenous land claims

-
 'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
'We are ghosts': Britain's migrant night workers
-
Asian markets rise as US inflation eases, Micron soothes tech fears

-
 Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
Trump signs $900 bn defense policy bill into law
-
EU-Mercosur deal delayed as farmers stage Brussels show of force

-
 Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
Harrison Ford to get lifetime acting award
-
Trump health chief seeks to bar trans youth from gender-affirming care

-
 Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
Argentine unions in the street over Milei labor reforms
-
Brazil open to EU-Mercosur deal delay as farmers protest in Brussels

-
 Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
Brussels farmer protest turns ugly as EU-Mercosur deal teeters
-
US accuses S. Africa of harassing US officials working with Afrikaners

-
 ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
ECB holds rates as Lagarde stresses heightened uncertainty
-
Trump Media announces merger with fusion power company

-
 Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
Stocks rise as US inflation cools, tech stocks bounce
-
Zelensky presses EU to tap Russian assets at crunch summit

-
 Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
Danish 'ghetto' residents upbeat after EU court ruling
-
ECB holds rates but debate swirls over future

-
 Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
Bank of England cuts interest rate after UK inflation slides
-
Have Iran's authorities given up on the mandatory hijab?

-
 British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
British energy giant BP extends shakeup with new CEO pick
-
EU kicks off crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine

-
 Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
Sri Lanka plans $1.6 bn in cyclone recovery spending in 2026
-
Most Asian markets track Wall St lower as AI fears mount

-
 Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
Danish 'ghetto' tenants hope for EU discrimination win
-
What to know about the EU-Mercosur deal

-
 Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
Trump vows economic boom, blames Biden in address to nation
-
ECB set to hold rates but debate swirls over future

-
 EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
EU holds crunch summit on Russian asset plan for Ukraine
-
Nasdaq tumbles on renewed angst over AI building boom

-
 Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
Billionaire Trump nominee confirmed to lead NASA amid Moon race
-
CNN's future unclear as Trump applies pressure


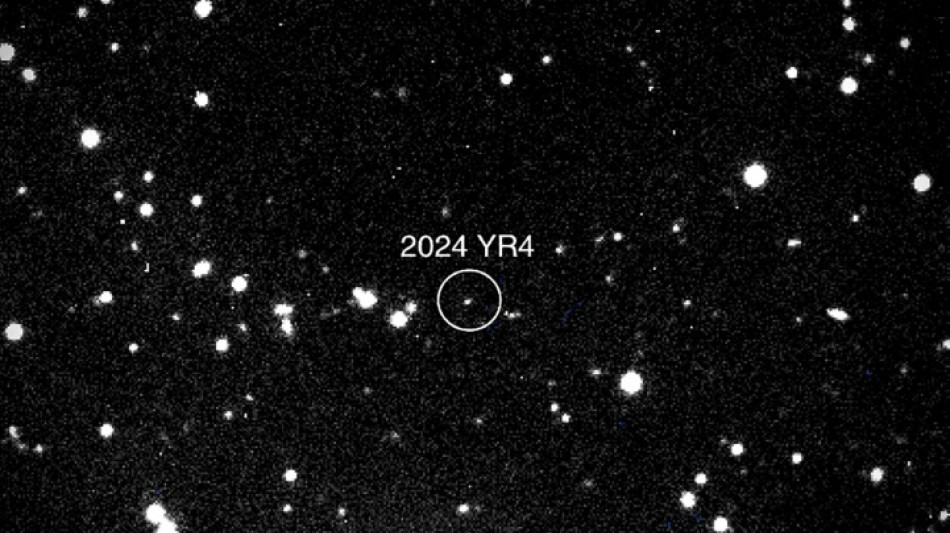
'City killer' asteroid now has 3.1% chance of hitting Earth: NASA
An asteroid that could level a city now has a 3.1 percent chance of striking Earth in 2032, according to NASA data released Tuesday -- making it the most threatening space rock ever recorded by modern forecasting.
Despite the rising odds, experts say there's no need for alarm. The global astronomical community is closely monitoring the situation and the James Webb Space Telescope is set to fix its gaze on the object, known as 2024 YR4, next month.
"I'm not panicking," Bruce Betts, chief scientist for the nonprofit Planetary Society told AFP.
"Naturally when you see the percentages go up, it doesn't make you feel warm and fuzzy and good," he added, but explained that as astronomers gather more data, the probability will likely edge up before rapidly dropping to zero.
2024 YR4 was first detected on December 27 last year by the El Sauce Observatory in Chile.
Astronomers estimate its size to be 130 to 300 feet (40–90 meters) wide, based on its brightness. Analysis of its light signatures suggests it has a fairly typical composition, rather than being a rare metal-rich asteroid.
The International Asteroid Warning Network (IAWN), a worldwide planetary defense collaboration, issued a warning memo on January 29 after the impact probability had crossed one percent. Since then, the figure has fluctuated but continues to trend upward.
NASA's latest calculations estimate the impact probability at 3.1 percent, with a potential Earth impact date of December 22, 2032.
That translates to odds of one in 32 -- roughly the same as correctly guessing the outcome of five consecutive coin tosses.
The last time an asteroid of greater than 30 meters in size posed such a significant risk was Apophis in 2004, when it briefly had a 2.7 percent chance of striking Earth in 2029 -- a possibility later ruled out by additional observations.
Surpassing that threshold is "historic," said Richard Moissl, head of the European Space Agency's planetary defense office, which puts the risk slightly lower at 2.8 percent.
- Webb observations in March -
"It's a very, very rare event," he told AFP, but added: "This is not a crisis at this point in time. This is not the dinosaur killer. This is not the planet killer. This is at most dangerous for a city."
Data from the Webb telescope -- the most powerful space observatory -- will be key in better understanding its trajectory, said the Planetary Society's Betts.
"Webb is able to see things that are very, very dim," he said -- which is key because the asteroid's orbit is currently taking it out towards Jupiter, and its next close approach won't be until 2028.
Unlike the six-mile-wide (10-kilometer-wide) asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago, 2024 YR4 is classified as a "city killer" -- not a global catastrophe, but still capable of causing significant destruction.
Its potential devastation comes less from its size and more from its velocity, which could be nearly 40,000 miles per hour if it hits.
If it enters Earth's atmosphere, the most likely scenario is an airburst, meaning it would explode midair with a force of approximately eight megatons of TNT -- more than 500 times the power of the Hiroshima bomb.
But an impact crater can't be ruled out if the size is closer to the higher end of estimates, said Betts.
If it does hit, possible impact sites include over the eastern Pacific Ocean, northern South America, the Atlantic Ocean, Africa, the Arabian Sea, and South Asia, the IAWN memo states.
The good news, experts emphasize, is that there is ample time to prepare. If necessary, spacecraft could be sent to deflect the asteroid -- technology that was successfully demonstrated in NASA's 2022 DART mission, which altered the course of a non-threatening asteroid.
Y.Jeong--CPN


